Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Learn to define file encryption with this clear guide. Discover how it works, its benefits, and how to protect your digital files in the cloud and beyond.
Let’s cut to the chase: file encryption is simply the process of turning a normal, readable file into a jumbled-up, secret code. Think of it like taking a private diary and rewriting it in a language only you can understand. To anyone else, it's just gibberish. This principle is universal, whether you're securing data in New York, Tokyo, or Berlin.

At its heart, file encryption is a security measure that scrambles your data. Let's say you have a sensitive spreadsheet full of financial numbers. When you encrypt it, you’re not just password-protecting it; you’re fundamentally transforming its contents into an unreadable mess called ciphertext.
This ensures that even if a hacker breaches your system or someone swipes your laptop, all they get is a block of useless characters. The only way to convert that gibberish back into the original, readable spreadsheet is with a specific digital "key."
In a globalized world where we keep everything from family photos to confidential business plans in digital form, this layer of security is non-negotiable. It’s your first and best line of defense against prying eyes, regardless of their location.
File encryption tackles a few critical security needs all at once:
Think of encryption as your personal digital safe. Anyone might be able to find the safe, but only the person with the correct key can actually open it and see what's inside.
This concept is a cornerstone of smart digital habits and an essential part of any international keyword strategy focused on security. In fact, solid file encryption is a key part of modern document management best practices, helping everyone from individuals to multinational corporations protect their most valuable information. Getting this basic principle down is the first real step toward securing your digital life.
So, how does a file go from something anyone can read into a protected secret? The entire process comes down to two things: an encryption algorithm and an encryption key.
Think of it like one of those secret decoder rings you had as a kid. The algorithm is the permanent, built-in design of the ring itself—the unchangeable system it uses to scramble letters. The key is the specific setting you choose for the day, like deciding that 'A' will stand for 'D'. Without knowing that exact setting (the key), any message you create is just meaningless gibberish to everyone else.
This is the fundamental idea behind turning a readable file into a protected one.
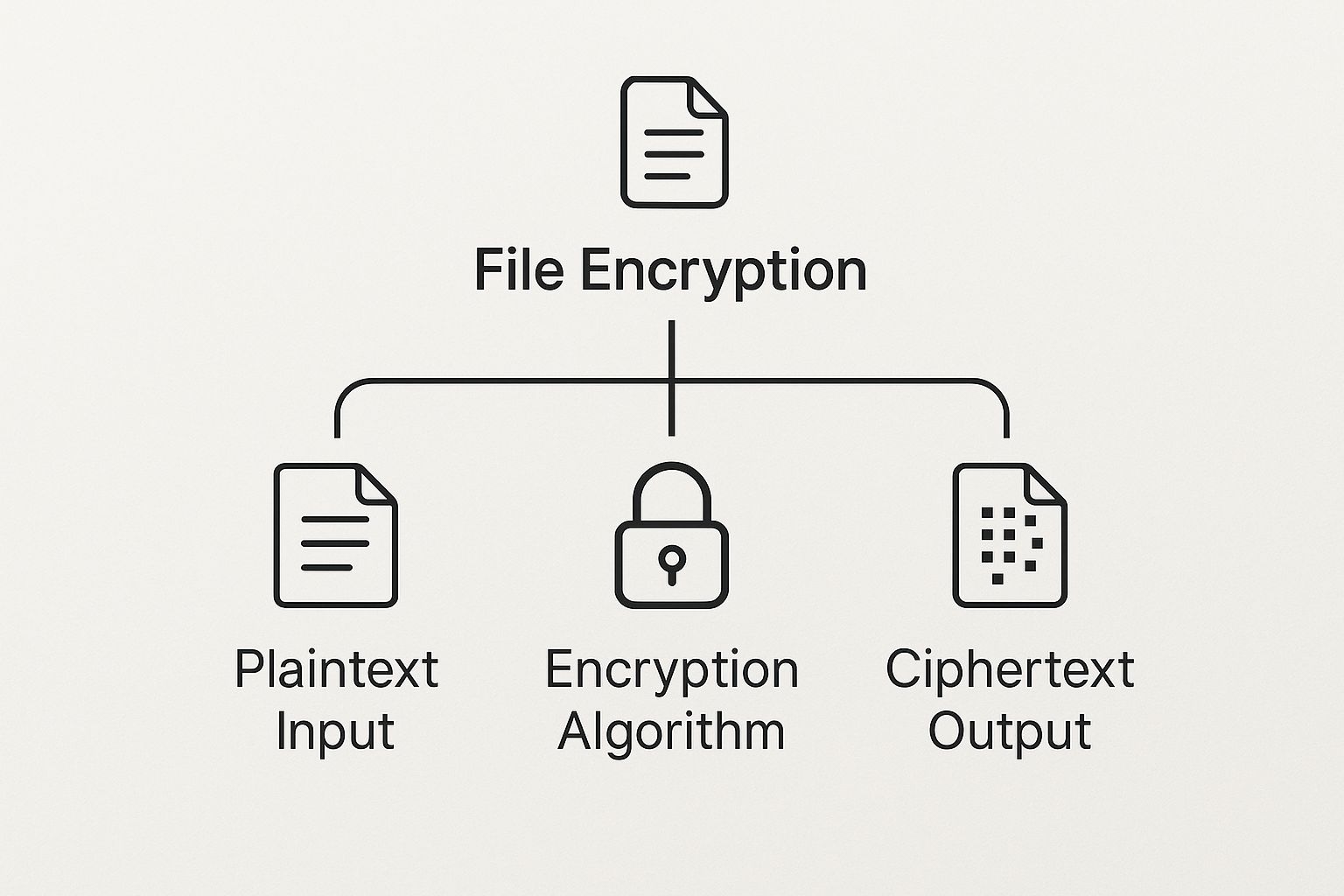
As you can see, your original data (plaintext) gets fed into the algorithm along with a key. What comes out the other side is scrambled, unreadable ciphertext. To unlock it, you just run the process in reverse with the same key.
The real magic, and where modern security gets its strength, is in how these keys are managed. There are two main ways to do it, and each has its own strengths and weaknesses.
To make this crystal clear, let's break down the core differences.
This table offers a quick side-by-side look at how these two crucial encryption methods stack up.
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Keys | One single shared key | A pair of keys (one public, one private) |
| Speed | Very fast and efficient | Slower due to more complex math |
| Key Management | The biggest challenge is sharing the key securely | Simpler; you can share the public key freely |
| Best For | Encrypting large amounts of data at rest (like on a hard drive) | Securely exchanging keys and verifying identities |
Ultimately, both types are vital. Symmetric encryption is great for raw speed, while asymmetric encryption provides the foundation for secure communication and identity verification across borders.
Key Takeaway: Asymmetric encryption is what makes secure digital life possible. It's the engine behind incredibly safe processes like encrypted file sharing, which protects your data when you send it to others. You can post your public key on a billboard, and it wouldn't compromise your security one bit.

When you're looking at a security tool to protect your files, you’ll almost always run into a few acronyms like AES and RSA. These aren't companies, but the "brand names" of the specific encryption algorithms doing the heavy lifting behind the scenes. Knowing what they are helps you appreciate just how strong the security protecting your data really is.
It’s important to know that each algorithm has a specific job. You wouldn't use a hammer to turn a screw, and in the same way, you wouldn't use every encryption method for the same task. The two you’ll encounter most often are AES and RSA, and they work in completely different ways.
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is the undisputed champion of symmetric encryption. It’s so trusted, in fact, that the U.S. government uses it to protect classified information. When you see a service like Sky Drive Folder mention it uses AES-256, it means your files are being scrambled with an incredibly strong 256-bit key.
Because it uses a single key for both locking and unlocking data (symmetric), AES is lightning-fast and efficient. This makes it the perfect choice for encrypting large files or even entire hard drives without grinding your computer to a halt.
On the other side of the coin is RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman), one of the original and most popular asymmetric encryption algorithms. Unlike AES, RSA uses a clever two-key system: a public key to encrypt data and a private key to decrypt it.
You can freely share your public key with anyone, and they can use it to send you a secure file. But here’s the magic: only your secret private key can unlock it. This makes RSA the backbone of secure online communication, from establishing a secure connection to a website (that little lock icon in your browser) to verifying digital identities, a critical component of technical SEO for international reach.
Both of these encryption methods are vital for a complete security system. Think of it this way: AES does the heavy lifting of scrambling the data itself, while RSA often works in the background to securely hand over the AES key in the first place, making sure no one can intercept it.
Beyond the nuts and bolts of how it works, the real-world reasons for encrypting your files are what make it an absolute must-do. This isn't just a technical exercise for IT experts; understanding why you should make file encryption a standard part of your life is key to protecting yourself. The reasons are simple, practical, and incredibly powerful.
The most obvious win is confidentiality. Think about it: if someone steals your laptop or breaks into your cloud account, encrypted files are completely worthless to them. Instead of getting your private documents or sensitive client data, they get a screen full of gibberish. All their effort is for nothing.
Next up is data integrity. Encryption acts like a tamper-proof seal on a physical document. It guarantees that the file you're looking at hasn't been secretly altered or corrupted since it was last saved. This is critical for everything from legal contracts to financial spreadsheets, where one tiny, unnoticed change could have massive consequences.
Finally, there’s compliance. For any business, using encryption isn't just a good idea—it's often the law. Regulations like GDPR in Europe, PIPEDA in Canada, and HIPAA in the US have strict rules about protecting customer and patient data. Failing to do so can lead to crippling fines and a total loss of trust, which is why localized content addressing regional data laws is so crucial. For individuals, it's about making sure your personal information stays exactly that: personal.
By making encryption a non-negotiable step, you create a formidable barrier against data breaches. It transforms your files from open books into locked digital vaults, accessible only to those with the right key.
This urgent need for better security is fueling major growth in the industry. The encryption software market, valued at around USD 13.45 billion recently, is on track to hit USD 30.44 billion by 2029. That number tells a clear story: the world is making a huge shift toward prioritizing data privacy. Successful multilingual outreach often hinges on demonstrating this commitment to security.
Ultimately, encryption is the foundation of digital trust. When you need to collaborate or send information, knowing how to share files securely starts with a solid encryption strategy, giving both you and your recipient genuine peace of mind.

Using cloud storage like Google Drive or Dropbox feels as natural as breathing these days, but it begs a serious question: is your data actually safe up there? The incredible convenience of the cloud operates on a principle called the shared responsibility model.
Think of your cloud provider as the owner of a high-tech storage facility. They’re responsible for the building’s security—the thick walls, the steel gates, and the guards at the door. But you are still responsible for putting a lock on your own storage unit. It's a simple distinction, but a critical one.
By default, most cloud services give you what’s known as encryption at-rest. This means once your file lands on their servers, it’s scrambled and protected. If someone were to physically steal the hard drive, they’d just find a jumble of useless code. That’s a good start, but there's a catch: the provider still holds the encryption key.
For true, uncompromising privacy, you need client-side encryption. This is a game-changer. You encrypt the file on your own computer before it ever leaves your device for the cloud. You—and only you—hold the key.
By using client-side encryption, you transform a public cloud service into your own private digital vault. The provider only stores a meaningless, scrambled block of data, giving you absolute control over who can access your most sensitive information.
This level of control is more important than ever. With the boom in cloud computing and remote work, strong file encryption has become a non-negotiable part of securing data for businesses and individuals alike. It's a key factor in conversion optimization per region, as users in privacy-conscious areas like the EU are more likely to trust services that offer client-side encryption.
Comparing how different cloud services handle your privacy is a vital step before you commit. To see how the major players stack up on security, check out our guide on the top cloud storage comparison. Ultimately, taking control of your own encryption keys is the only way to ensure your files in the cloud remain truly yours.
Knowing what file encryption is is one thing, but actually using it is what keeps your data safe. The good news? You don’t need a degree in cybersecurity to get started. Powerful and surprisingly simple tools are likely already built into the computer you’re using right now.
The easiest way to begin is with your operating system’s native encryption. These features are designed to be "set it and forget it," providing a rock-solid security baseline for your entire device.
For more specific tasks, like protecting individual files before you upload them to the cloud or send them to a colleague, third-party software gives you more granular control. Tools like AxCrypt or VeraCrypt let you encrypt specific files or even create secure digital “vaults” for your most sensitive documents. This is the perfect approach for locking down financial records or confidential project files. This kind of hands-on security is one of the content types that drive global conversions, as it empowers users directly.
The key is to match the method to your goal. Full-disk encryption is fantastic for securing a physical device, while file-specific tools are essential for protecting data as it moves between different people and places.
A lot of the apps you already use daily also handle encryption behind the scenes. Secure messaging apps lock down your conversations, and many cloud services offer built-in security. When you’re sending files, it's absolutely critical to use a platform that protects your data from start to finish. You can learn more about how to do this in our guide on achieving a secure online file transfer, which covers the best practices for keeping your files safe while they're in transit.
Of course. Here is the rewritten section, crafted to sound like it was written by an experienced human expert, following your provided style and formatting guidelines.
Once you get the hang of the basics, a few practical questions almost always pop up. It's one thing to understand the theory, but another to feel confident using it day-to-day. Let's clear up some of the most common points of confusion so you can start protecting your files without hesitation.
The most important thing to remember is that you're in the driver's seat.
Yes, and this is the one part you absolutely have to get right. If you lose your encryption key or forget the password, that file is gone for good.
Think of it like losing the only key to a real-world bank vault—there’s no master key, no locksmith, and no secret backdoor. This is why managing your keys and recovery phrases with extreme care isn't just a suggestion; it's essential.
This is a common worry, but thankfully, it's mostly a myth these days. Modern computers and encryption algorithms are built for speed.
While a tiny bit of processing power gets used when you actively encrypt or decrypt a file, you'll almost certainly never notice it during your normal work. The immense security boost you get is well worth the nearly invisible performance cost.
The key takeaway is that strong encryption doesn't have to be a burden. Modern tools are designed to work seamlessly in the background, protecting your data without interrupting your workflow.
So, what's the difference between locking up a single file versus your entire hard drive? It comes down to what you’re trying to protect against.
Ready to secure your files with military-grade encryption and seamless sharing? Sky Drive Folder offers robust AES-256 encryption for all your data, both at-rest and in-transit, ensuring your files are protected from every angle. Take control of your digital privacy today by visiting https://skydrivefolder.com to start your secure journey.
[…] from interception. To fully grasp email encryption, it's beneficial to first understand the basic principles of encryption and how it transforms readable data into an unreadable […]