Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Discover the top 10 secure file transfer methods for 2025. This guide covers SFTP, MFT, and more for robust, global data protection and sharing.
In a globalised economy, moving data securely and efficiently is no longer a luxury, it's a fundamental operational requirement. Whether you're a freelancer sending large media assets, a remote team collaborating on sensitive projects, or a business exchanging critical partner data, standard email attachments often fall short on both security and reliability. The consequences of a data breach or a failed transfer can be significant, impacting everything from project timelines to client trust and regulatory compliance. For those evaluating various data exchange methods, a fundamental question often arises: Is Fax More Secure Than Email? This comparison highlights the need for specialized tools built for specific security and transfer challenges.
This guide moves beyond basic file sharing to provide a comprehensive overview of ten powerful and secure file transfer methods. We will analyse everything from established protocols like SFTP and FTPS to modern solutions involving cloud APIs and blockchain technology. For each method, you will find a clear breakdown of its core function, practical pros and cons, and real-world scenarios where it excels. This article is designed to equip you with the knowledge to select and implement the right transfer solution for your specific needs, ensuring your data remains protected and accessible, wherever it needs to go.
SFTP stands as a cornerstone among secure file transfer methods, operating over the robust SSH (Secure Shell) protocol. Unlike its predecessor, FTP, SFTP encrypts both commands and data in transit, preventing passwords and sensitive information from being exposed. This protocol establishes a single, secure connection for authentication, commands, and file transfers, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality from end to end.
For international teams, SFTP is particularly valuable. It allows businesses to securely manage localized content on servers in different countries, which is a key part of an effective international keyword strategy. For example, a financial institution can use SFTP to securely exchange documents between its Canadian headquarters and European branches, with each server’s SSH configuration tailored to local regulations.
SFTP’s reliability and security make it a preferred choice for many critical operations. Major code repositories like GitHub and cloud services like AWS SFTP leverage it for secure access and file management. It's an indispensable tool for technical SEO for international reach, allowing teams to securely update and manage website files—including multilingual sitemaps—across a global network of servers.
chroot jail to confine users to their home directories, preventing them from navigating the server’s entire file system. This is a vital step in a multi-user environment.The following infographic highlights SFTP's core security and reliability features.
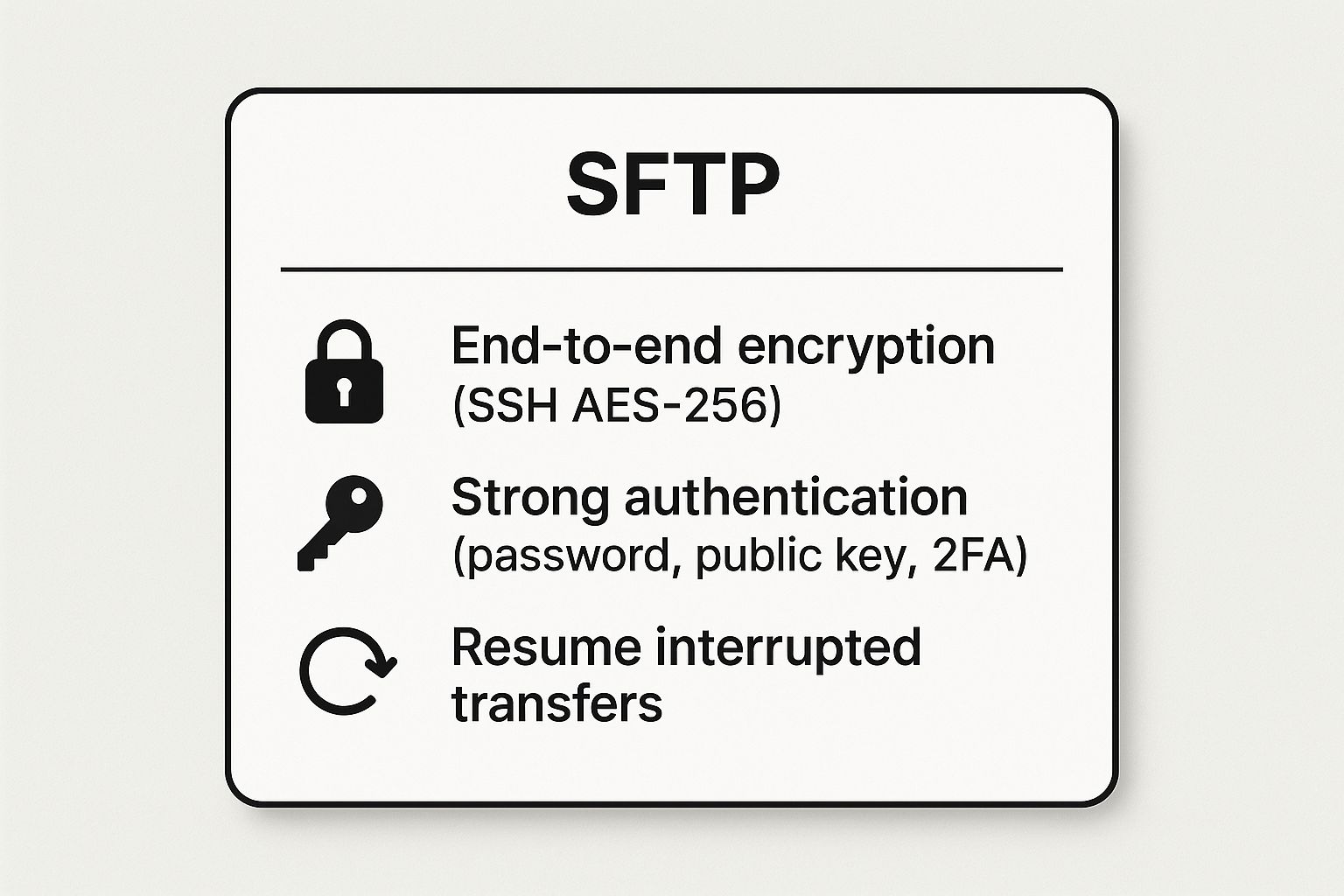
These three pillars-encryption, authentication, and transfer resilience-make SFTP a highly dependable method for secure file transfers, especially for businesses requiring systematic, automated, and auditable data exchanges.
FTPS adds a vital layer of security to the classic File Transfer Protocol by incorporating Transport Layer Security (TLS), the successor to SSL. Unlike SFTP, which uses a completely different protocol (SSH), FTPS enhances the existing FTP framework, encrypting the command and data channels to protect credentials and files during transfer. This approach offers backward compatibility while providing the robust encryption necessary for modern secure file transfer methods.
For global enterprises, FTPS is a practical solution for securing data exchanges with partners who may still rely on traditional FTP infrastructure. A manufacturing company, for example, can use FTPS to securely share large CAD files with international suppliers. By leveraging TLS, they can meet regional data protection requirements and ensure that sensitive intellectual property is protected across borders, a key component of technical SEO for international reach and maintaining a secure global supply chain.
The primary advantage of FTPS is its ability to secure legacy workflows, making it popular in industries like banking, e-commerce, and media. Financial institutions rely on it for secure data exchange, and e-commerce platforms use it for updating product catalogues. Its implementation in popular clients like FileZilla and servers like Microsoft IIS has solidified its place as a dependable transfer method. For a deeper look into its applications, you can explore various resources on secure online file transfer.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) represents one of the most accessible and widely used secure file transfer methods today. It leverages the standard web protocol (HTTP) but adds a layer of security through SSL/TLS encryption. This ensures that any data, including files being uploaded or downloaded, is encrypted between the user's browser and the server, protecting it from interception. Its ubiquity makes it the default choice for countless web applications, from cloud storage to online collaboration tools.
For global businesses, HTTPS is fundamental to creating a seamless and secure user experience. Platforms like Google Drive and Dropbox use it to allow users worldwide to upload and share files directly from their web browser. This accessibility is vital for businesses using geo-targeted landing pages to securely collect customer information or for marketing teams distributing content types that drive global conversions, all while maintaining compliance with data protection laws like PIPEDA in Canada.
The simplicity and browser-native support of HTTPS make it ideal for user-facing applications. Major cloud storage providers such as Microsoft OneDrive and enterprise document management systems rely on it for their core functionality. It is the backbone for any business that needs to offer secure, ad-hoc file sharing to clients or team members without requiring them to install specialized software.
The core pillars of HTTPS transfers-accessibility, encryption, and user-friendliness-make it an indispensable method for modern web-based file sharing. It provides a secure, intuitive, and universally compatible solution for both personal and professional use cases, simplifying secure data exchange across the globe.
AS2 is a highly structured protocol designed specifically for secure and reliable business-to-business (B2B) data exchange. Operating over HTTP/HTTPS, it provides a standardized method for transmitting sensitive data, such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) documents. AS2 ensures data integrity and confidentiality through digital signatures and encryption, and its core feature is the Message Disposition Notification (MDN), which acts as a legally binding receipt confirming a message was successfully received and decrypted.
This protocol is foundational for global supply chains. For instance, major retailers like Walmart mandate its use for suppliers to standardise communication and ensure timely, verifiable order processing. An international manufacturer can leverage AS2 to connect its global operations, ensuring all partners adhere to the same secure file transfer methods for purchase orders and invoices. This level of transactional integrity is crucial for conversion optimization per region by streamlining business processes.
AS2's strength lies in its non-repudiation and real-time transaction capabilities, making it indispensable for mission-critical document exchanges. It is heavily utilized in retail, automotive, healthcare, and financial services, where proof of delivery and data integrity are paramount. Platforms like IBM Sterling and Microsoft BizTalk Server have popularised its implementation across enterprise-level systems.
Managed File Transfer (MFT) represents a centralised platform rather than a single protocol. It provides a comprehensive solution for securely managing, monitoring, and automating all file transfer activities within an organisation. MFT solutions integrate multiple secure protocols like SFTP, FTPS, and HTTPS under a single management umbrella, adding layers of governance, compliance reporting, and advanced workflow automation.
For organisations operating globally, MFT is a game-changer. It allows enterprises to enforce consistent security policies while adapting to regional data sovereignty laws. For instance, a multinational corporation can use an MFT solution to automate the distribution of localized content to regional servers, supporting a cohesive international keyword strategy. This ensures all transfers are encrypted, logged, and compliant with privacy regulations, as seen in Hook Security's strategic partnership with Sendsafely for secure file transfer.
MFT’s main strength lies in its ability to provide visibility and control over complex data exchanges. Major players like IBM (Sterling File Gateway) and Progress Software (MOVEit) are staples in finance and government, where audit trails and guaranteed delivery are non-negotiable. It’s an essential tool for any business needing to manage high-volume, mission-critical file transfers with robust security and operational insight.
These core capabilities of automation, central governance, and enhanced security make MFT an indispensable platform for enterprises seeking to modernise and secure their file transfer infrastructure. For more information on this topic, learn more about team file sharing solutions.
End-to-End Encrypted (E2EE) email offers a surprisingly robust framework among secure file transfer methods, embedding security directly into everyday communication. Unlike standard email, E2EE systems encrypt messages and attachments on the sender's device and ensure they can only be decrypted by the intended recipient. This process guarantees that no one in between, not even the email provider, can access the content, making it a highly private way to share sensitive files.
For organisations with a global footprint, E2EE email is an effective tool for maintaining data privacy across borders. Legal firms, for example, can use PGP-based encryption to securely exchange confidential case files with international clients, ensuring attorney-client privilege is upheld regardless of jurisdiction. This aligns with a technical SEO strategy for international reach, where demonstrating high security standards can build trust with a global audience and support efforts like backlink building in target regions by protecting sensitive outreach communications.
E2EE email's strength lies in its user-centric privacy controls, making it ideal for scenarios where confidentiality is paramount. Services like ProtonMail and Tutanota have popularised this method for both privacy-focused individuals and businesses. It is commonly used by healthcare organisations to send patient data in compliance with HIPAA and by journalists protecting their sources. This method is explored further in our guide on how to share files securely.
These core principles of user-controlled encryption and transit security make E2EE email a powerful and accessible option for secure file transfers, particularly for ad-hoc sharing of sensitive documents where audit trails are managed at the user level.
Secure cloud storage APIs offer programmatic access to major cloud platforms, enabling direct integration of file transfer capabilities into applications and workflows. Rather than manual uploads, these APIs allow for automated, secure data exchanges with services like AWS S3 or Google Cloud Storage. They leverage the cloud provider’s native security infrastructure, including robust authentication, access control, and encryption for data both in transit and at rest, making them a highly scalable secure file transfer method.
This approach is invaluable for businesses operating globally. A company can use the Microsoft Azure Blob Storage API to build geo-targeted content delivery systems, ensuring that user data is stored and processed within specific regions to comply with local data sovereignty laws. This allows for optimized performance and helps in creating localized user experiences, a key part of technical SEO for international reach and conversion optimization per region.
Cloud storage APIs are the backbone of modern cloud-native applications, from enterprise data lakes to collaborative software. Services like the Box API and Dropbox Business API are widely used to build secure content management and workflow automation into business-critical platforms. These APIs provide a powerful method for handling large-scale, automated file transfers securely and efficiently. For more information, you can learn more about encrypted file sharing with cloud services.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates an encrypted tunnel between a user's device and a private network, allowing standard file transfer protocols to operate securely over public networks like the internet. Instead of being a transfer protocol itself, a VPN acts as a protective layer, encrypting all data traffic that passes through it. This makes it one of the most versatile secure file transfer methods for remote and distributed workforces.

For global businesses, a VPN is essential for enabling secure access to internal file servers from anywhere in the world. An international marketing team can use a VPN to connect to their company’s central server, allowing them to access localized content and geo-targeted landing pages as if they were physically in the office. This ensures that sensitive project files and proprietary data remain confidential, regardless of the employee's location.
VPNs are widely adopted by organisations of all sizes, from enterprises like Cisco to open-source solutions like OpenVPN and modern protocols like WireGuard. They are critical for healthcare networks needing to access patient data from remote clinics and for financial institutions requiring secure connections for trading operations. The VPN model is foundational for enabling a secure perimeter for a distributed workforce.
The combination of data encryption, remote access, and network security makes VPN-based transfers a reliable solution for organisations needing to extend their private network securely to remote employees and branch offices.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) encrypted transfer offers a decentralized approach among secure file transfer methods, enabling direct file sharing between devices without a central server. This model leverages cryptographic protocols to encrypt data directly on the sending device and decrypt it only on the recipient's machine. By eliminating the intermediary server, P2P transfers can enhance privacy, reduce potential points of failure, and often provide faster speeds for large files.
For international collaboration, this method is highly effective. A distributed team can use a tool like Resilio Sync to keep project files synchronized across different countries without routing all data through a single, distant headquarters. This setup helps manage large media assets for global marketing campaigns or synchronizes multilingual documentation across regional engineering teams, ensuring everyone has the latest version while respecting local data handling preferences.
P2P's direct-connect nature makes it ideal for rapid, secure sharing of sensitive information or bulky files. Solutions like Syncthing and Magic Wormhole are popular for continuous file synchronization and one-off secure transfers, respectively. This method supports technical SEO for international reach by allowing web development teams to quickly distribute and update geo-targeted website assets across a private, secure network of devices.
The combination of speed, decentralization, and robust encryption makes P2P a powerful choice for teams and individuals needing resilient and private file sharing capabilities without reliance on third-party infrastructure.
Blockchain-based file transfer represents a paradigm shift in how we think about secure file transfer methods, utilizing distributed ledger technology for decentralized security. Instead of relying on a central server, this method breaks files into encrypted pieces and distributes them across a peer-to-peer network. Each transfer and file modification is recorded as a transaction on an immutable blockchain, creating a transparent and tamper-proof audit trail.
This decentralized model offers unique advantages for organizations focused on a global presence and data resilience. By removing single points of failure, it ensures high availability and censorship resistance, which is critical for content that needs to be accessible worldwide without restriction. For example, a company creating geo-targeted landing pages can use a platform like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) to ensure localized content is served efficiently and reliably to users in any region.
The core appeal of blockchain transfers is their unparalleled security through decentralization and cryptographic verification. Platforms like Storj, Filecoin, and Sia exemplify this approach, creating robust marketplaces for decentralized storage and file sharing. This model is particularly effective for technical SEO for international reach, where permanent and verifiable content hosting can enhance credibility and performance across diverse markets, supporting a strong international keyword strategy.
These pillars of decentralization, immutability, and user-controlled encryption make blockchain-based systems a compelling option for those needing maximum security, transparency, and resilience in their file transfer strategy.
| Technology | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) | Medium – Requires SSH setup and config | Moderate – SSH server and keys | Secure, encrypted file transfers with integrity verification | Enterprise transfers, automated backups, secure remote access | Strong encryption, resume interrupted transfers, firewall-friendly |
| FTPS (FTP Secure/FTP-SSL) | Medium-High – SSL cert management and firewall config | Moderate – SSL certificates and ports | Secure file transfers with backward FTP compatibility | Legacy systems, B2B transfers, batch processing | Familiar FTP interface, good large file performance |
| HTTPS File Upload/Download | Low – Web server and HTTPS setup | Low – Web server and API support | Universal secure file sharing via browsers and APIs | Web apps, consumer sharing, mobile, cloud storage | Universal browser support, firewall-friendly, easy to use |
| AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) | High – Complex setup and cert management | High – Specialized software and expertise | Secure, real-time B2B document exchange with audit trails | B2B EDI transactions, supply chain, finance, healthcare | Strong security, delivery receipts, audit trails |
| Managed File Transfer (MFT) | Very High – Enterprise-grade deployment | High – Dedicated IT and licensing | Centralized, automated, compliant secure transfers | Enterprise governance, compliance, workflow automation | Multi-protocol support, centralized management, scalability |
| End-to-End Encrypted Email | Medium – Key management required | Low to Moderate – Depends on system | Confidential file sharing with strong E2E encryption | Legal docs, confidential communications, small file sharing | Familiar interface, strong encryption, no extra infra |
| Secure Cloud Storage APIs | Medium – API integration and auth | Moderate – Cloud infrastructure | Scalable, integrated secure storage and transfer | Application integration, automated backups, content delivery | Scalable, reliable, pay-as-you-go, encryption |
| VPN-Based File Transfer | High – Network and VPN config | High – VPN infrastructure and maintenance | Secure network-level file transfers, any protocol supported | Remote access, site-to-site, branch integration | Network-wide encryption, protocol agnostic, centralized control |
| Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Encrypted Transfer | High – NAT/firewall traversal and setup | Low to Moderate – Depends on peers | Direct encrypted file sharing, decentralized, resilient | Large file distribution, remote sync, anonymous transfers | No central server, scalable, privacy-focused |
| Blockchain-Based File Transfer | Very High – Blockchain and storage integration | High – Distributed storage and blockchain nodes | Immutable, decentralized file sharing with auditability | Archival, content distribution, decentralized apps | Immutable audit trail, censorship-resistant, smart contracts |
Navigating the landscape of secure file transfer methods can feel like charting a course through uncharted waters. As we've explored, the digital world offers a rich tapestry of options, from the battle-tested resilience of SFTP and FTPS to the modern, decentralized security of blockchain-based transfers. The key takeaway is not that one method reigns supreme, but that the right method is entirely dependent on your specific context, threat model, and operational needs.
Your decision-making process should be a strategic one, moving beyond a simple feature comparison. It's about building a framework that aligns with your unique requirements, whether you're a freelancer sending large design files, a small business managing sensitive client data, or a global enterprise coordinating across multiple regions. The most effective approach often involves a hybrid strategy, leveraging multiple secure file transfer methods for different tasks.
To move from understanding to implementation, consider these critical factors as a final checklist:
The journey toward mastering secure data transit begins with a single, deliberate step. Start by auditing your current file sharing practices. Identify where sensitive information is being moved, by whom, and through what channels. This audit will reveal your biggest vulnerabilities and highlight the most urgent areas for improvement.
From there, create a simple "data sensitivity" matrix. Classify your data types (e.g., public, internal, confidential, restricted) and map them to the appropriate transfer methods we've discussed. This simple exercise provides immediate clarity and gives your team a practical playbook for handling different kinds of information securely. By thoughtfully selecting and implementing the right combination of secure file transfer methods, you transform data transfer from a potential liability into a secure, efficient, and reliable business asset.
Ready to implement a powerful, user-friendly solution that combines robust security with seamless collaboration? Sky Drive Folder offers an intuitive platform built for secure file sharing, storage, and management, perfect for teams and individuals. Simplify your workflow without compromising on security by exploring what Sky Drive Folder can do for you today.
Immerse into the expansive sandbox of EVE Online. Become a legend today. Create alongside millions of pilots worldwide. [url=https://www.eveonline.com/signup?invc=46758c20-63e3-4816-aa0e-f91cff26ade4]Play for free[/url]