Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Master secure online file transfer with proven strategies. Learn encryption, compliance, and deployment options that protect your data in today's digital world.
Let’s start with a simple, yet uncomfortable, truth: most people think their files are safe when they are actually quite vulnerable. Sending a file with a standard email attachment or a basic cloud link is like sending cash through the regular mail. It might get there, but you’re trusting that no one will intercept it along the way. A secure online file transfer is the digital version of an armored truck service—it’s built from the ground up to guard your valuable assets during their journey.

The methods we use out of habit are often the ones that create the biggest threats. Cybercriminals specifically target these common channels because they know they often lack strong protection. That seemingly harmless link to a project proposal or an attached invoice could be the exact opening a bad actor is looking for. Without the right security, these transfers are like digital whispers that can be easily overheard.
Moving files isn’t new, and neither are the original tools created for the job. One of the first methods was the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). While it was a foundational technology, standard FTP sends everything—including your username and password—in plain text. This means anyone watching the network traffic can read your information as easily as reading a postcard.
Here is a look at the historical context of FTP, which shows its design was created long before modern security became a primary concern.

The protocol has been around for decades, from a time when the internet was a much less hostile place. Its age explains why it doesn’t have the built-in encryption needed for today’s security challenges. To fix this, more secure protocols like FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) and SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) were created, adding the “armored truck” layers of protection that basic FTP was missing. You can explore our other articles to learn more about the specifics of safe and encrypted file transfers online.
How can you tell if your current method is putting you at risk? The warning signs are often hidden in plain sight. A lack of security options is a major red flag. If your file sharing tool doesn’t let you apply basic safeguards, you are likely exposed.
Consider these common vulnerabilities:
A growing awareness of these dangers is causing big changes across industries. This shift is clear in the market’s growth; the global secure file transfer market hit USD 2.4 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to about USD 3.7 billion by 2033. You can find more insights about this market growth on the IMARC Group’s website. This trend highlights a critical point: secure transfer is no longer a small-time need but a vital business practice.
The journey from a vulnerable file to a secure one relies on layers of digital protection working together. Think of this security arsenal as a fortress, where each component plays a specific role in defending your data. At its core is encryption, the process of scrambling your file’s data into an unreadable format. It’s like hiring a master locksmith to create a unique, complex lock for your digital document. Only someone holding the perfectly crafted key can unlock and read its contents. This fundamental process is the foundation of any trustworthy secure online file transfer system.
This concept is brought to life through specific encryption standards. The most widely trusted standard today is AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard with a 256-bit key). Adopted by the U.S. government and used globally to protect classified information, its strength is staggering. A 256-bit key has more possible combinations than there are atoms in the known universe, making a brute-force attack practically impossible with current technology.
Here is a visual representation of how AES processes data in blocks, applying multiple rounds of transformation to ensure its security.
This diagram shows the complex, multi-step process that makes AES so robust, turning plain text into incomprehensible ciphertext.
Encryption isn’t a one-size-fits-all tool. There are two primary methods, each with a distinct purpose, similar to how you might use different types of keys for your home.
While encryption protects the file itself, another layer of security is needed to protect the connection it travels through. This is where protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) come in. TLS creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and the server, ensuring that no one can eavesdrop on the transfer while it’s in motion. It’s the armored truck that transports your locked file safely to its destination. Without it, even an encrypted file could be vulnerable to certain attacks during transit.
Beyond encryption, a robust security system for file transfer includes several other critical checkpoints to verify identity and maintain integrity.
| Security Layer | Analogy | Purpose in Secure File Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | The Bouncer at a Club | Verifies that both the sender and receiver are who they claim to be, often through passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), or digital certificates. |
| Data Integrity | The Tamper-Evident Seal | Uses checksums or hashes to confirm that the file hasn’t been altered or corrupted during transfer. It ensures what you sent is exactly what was received. |
| Audit Trails | The Security Camera Log | Creates a detailed record of every action taken—who accessed a file, when, and from where. This is crucial for troubleshooting and proving compliance. |
Together, these elements create a multi-layered defense system. Encryption locks the file, TLS protects the journey, authentication verifies the identities, integrity checks ensure it arrives untouched, and audit trails record the entire event. This complete approach is what truly defines a secure online file transfer.
Navigating The Compliance Maze Without Losing Your Mind
Dealing with regulatory compliance can feel like trying to solve a puzzle in the dark. Rules like GDPR, HIPAA, and others have strict requirements for handling data, and using a secure online file transfer system is a fundamental part of meeting them. It’s helpful to think of these regulations not as obstacles but as blueprints for building trust. They give you a clear framework for protecting sensitive information, which is exactly what your customers and partners expect.

Key Regulations and What They Mean for Your Files
Understanding compliance begins with knowing the major players. Each regulation focuses on different kinds of data, but they all have a shared goal: protecting privacy and ensuring security, both when data is stored and when it’s on the move.
To better illustrate how these rules apply across different sectors, the table below breaks down the specific obligations for secure file transfer.
| Industry | Primary Regulation | Key Requirements | Data Types Protected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | HIPAA | End-to-end encryption, strict access controls, detailed audit trails, Business Associate Agreements (BAAs). | Protected Health Information (PHI), patient records, medical imaging, insurance claims. |
| Finance | SOX / GLBA | Data integrity controls, secure storage and transmission, access monitoring, proof of delivery. | Financial statements, customer financial data, non-public personal information (NPI). |
| E-commerce & Retail | PCI-DSS | Encrypted transmission of cardholder data over open networks, secure network configuration, access restriction. | Cardholder data (credit card numbers, names, expiration dates, security codes). |
| Technology & SaaS | GDPR / CCPA | Data protection by design, restrictions on cross-border data transfers, user consent for data processing. | Personal data of EU/California residents, user credentials, behavioral data. |
| Legal | ABA Model Rules | Duty of confidentiality, ensuring technology competence to protect client information from unauthorized access. | Attorney-client privileged communications, case files, discovery documents. |
Table: Industry Compliance Requirements for Secure File Transfer
Description: Comparison of key regulatory requirements across different industries and their specific secure file transfer obligations
This comparison shows that while the protected data types differ, the core requirements—encryption, access control, and auditability—are universal. Choosing a file transfer solution that addresses these common needs is a strong first step toward meeting compliance across the board.
True compliance is more than just encryption. Two critical, yet often overlooked, components are data residency and audit logs. Data residency is about where your data is physically stored. Some laws, such as GDPR, have strict rules about transferring personal data outside of certain geographic areas unless specific safeguards are in place. This means you need to know exactly where your file transfer provider’s servers are located.
At the same time, detailed audit logs serve as your proof of compliance. These logs aren’t just for show; they are your official record. They track every single action—who sent a file, who received it, when it was accessed, and from where. If regulators ever ask, a complete audit trail proves you have maintained full control and visibility over your sensitive data. The importance of these features is clear in market trends; the banking and financial services sector, driven by heavy regulation, leads in adoption. In fact, large enterprises, which make up 54.5% of the user base, invest significantly in compliant solutions to meet these demands.
The theory of secure data exchange is one thing, but seeing it in action is where its real value becomes clear. Every industry faces its own set of problems when sharing sensitive information, and their solutions for secure online file transfer are as specific as the challenges they face. From protecting patient privacy to safeguarding intellectual property, these specialized approaches turn security needs into a business advantage.

This screenshot from Wikipedia shows the basic idea behind cloud computing, the technology that drives many modern file transfer solutions. The cloud’s design allows for scalable and accessible data management, which is essential for industries that handle enormous amounts of information.
Imagine a pediatric hospital needs to share a large MRI scan. The file has to get from a radiologist at the main campus to a consulting specialist in another city. The file is huge, time-sensitive, and contains Protected Health Information (PHI). A simple email is neither secure nor practical for this task.
Instead, the hospital relies on a HIPAA-compliant file transfer platform. The MRI file is uploaded to a secure portal, where it is encrypted both during the transfer and while it sits on the server. The specialist can only access it after passing multi-factor authentication. This process ensures the hospital meets strict regulatory rules while also enabling faster, life-saving collaboration between doctors.
Think about a Hollywood studio that needs to send the final cut of a blockbuster movie to its international distributors. The file is gigantic—often several terabytes—and its value is immense. A leak could result in millions of dollars in lost revenue. To prevent this, the studio uses a managed file transfer (MFT) solution. This system offers:
This creates a secure and fully traceable digital supply chain for the studio’s most valuable assets.
A global manufacturing company working with parts suppliers around the world must share proprietary 3D CAD designs without risking them falling into the hands of competitors. Similarly, a law firm needs to exchange confidential case files during a high-stakes lawsuit. Both industries depend on solutions that provide end-to-end encryption and detailed audit trails.
For the manufacturer, this means a supplier can securely view a design file for a limited time, with every single action logged. For the law firm, it creates a defensible record of who accessed discovery documents, which is critical for legal proceedings.
The shift toward cloud and hybrid systems has made scalable platforms more important than ever. The world’s data creation is growing at a stunning rate; in 2024 alone, it hit 147 zettabytes, with an incredible 400 million terabytes being generated every day. To get a better sense of this data explosion and its market impact, you can explore the full industry analysis from Global Market Insights. This massive amount of data highlights why robust, industry-specific transfer solutions are no longer just a nice-to-have.
Deciding where your secure online file transfer system will live is more than just a technical detail—it’s a core strategic choice that shapes your security, budget, and operational agility. Making the wrong call here can lead to surprise costs and security vulnerabilities. Let’s explore the real-world impact of each deployment model.
Cloud-based solutions are much like renting a fully equipped, modern office. You pay a predictable fee, and the provider takes care of the rest: maintenance, security patches, and managing the infrastructure. This approach allows for quick setup and easy scalability, letting you get started without a huge upfront investment in hardware or a dedicated IT team. For many small businesses and teams, this is the most direct route to enterprise-level security.
This infographic shows how different file transfer tools stack up, often highlighting how cloud solutions provide top-tier features with a user-friendly design.
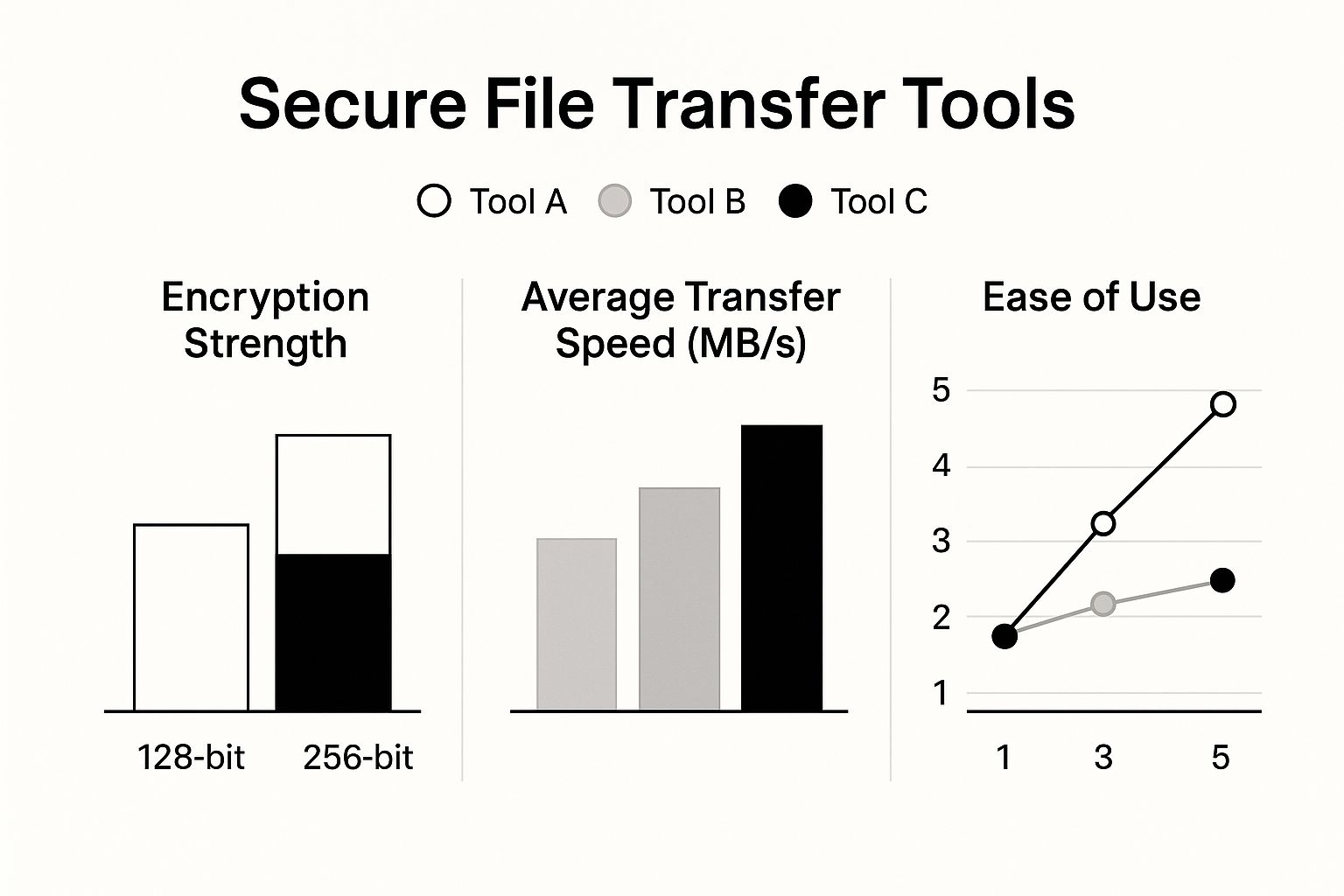
As the visual points out, a tool can deliver strong 256-bit encryption and high speeds without being complicated to use, which is a major benefit of leading cloud services.
An on-premises deployment is like building and owning your own fortress. You have absolute control over every single security measure, from the digital locks on your data to the virtual cameras monitoring traffic. This model gives you complete authority over your information, which is non-negotiable for organizations with stringent compliance needs or data sovereignty rules, like government agencies or defense contractors. You are responsible for managing all the hardware, software, and security protocols in-house.
This degree of control comes with a big investment in both infrastructure and the expert staff needed to run it. However, for organizations that simply cannot let sensitive data leave their direct physical control, it remains the go-to option. In fact, on-premises solutions accounted for 57% of the market share in 2023, largely because major enterprises need direct command over their systems. You can read more about these market trends and their drivers to see why this model is still so prevalent.
A hybrid model blends the tight control of on-premises with the agility of the cloud. Think of it as keeping your most priceless jewels in a personal safe at home while using a bank’s safety deposit box for other valuable items. Organizations adopt this strategy to store their most sensitive data—like intellectual property or patient records—on internal servers while using the cloud for less critical but frequent transfers, such as marketing materials or client communications.
This balanced approach helps fine-tune both security and cost, adapting to different types of data. It’s a particularly effective strategy when you need to securely transfer large files quickly, as you can tap into the cloud’s powerful infrastructure for tasks that demand high speed.
To help you decide which model fits your needs, here’s a detailed comparison of the different deployment options.
Detailed comparison of cloud, on-premises, and hybrid deployment options including costs, security features, and suitability for different organization types
| Deployment Type | Security Control | Scalability | Cost Structure | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Vendor-managed; strong encryption and compliance certifications are standard. | High; scale resources up or down on demand. | Subscription-based (OpEx); predictable monthly/annual fees. | SMBs, startups, and teams needing fast deployment and low initial investment. |
| On-Premises | Complete, granular control over all security policies and infrastructure. | Limited; scaling requires purchasing new hardware and lengthy setup. | High upfront capital expenditure (CapEx) for hardware, plus ongoing maintenance costs. | Large enterprises, government agencies, and industries with strict data sovereignty rules. |
| Hybrid | Balanced; high control for sensitive data on-prem, with cloud flexibility for other data. | Flexible; scale cloud resources as needed while maintaining a core on-prem system. | Mix of CapEx and OpEx; initial investment plus ongoing subscription costs. | Organizations with mixed data sensitivity that want to optimize both security and cost. |
This table shows there’s no single “best” option—it all depends on your organization’s specific needs for control, cost, and flexibility. Whether you need the turnkey convenience of the cloud, the absolute authority of an on-premises setup, or a balanced hybrid approach, the right choice is the one that aligns with your operational and security goals.
With countless solutions all claiming to be the best for secure online file transfer, finding the right one can feel like an impossible task. The key is to cut through the marketing noise and focus on a practical evaluation framework. Instead of getting dazzled by flashy features, start by looking at what truly matters: robust encryption, essential compliance certifications, and a proven track record of reliability. This approach is the first step toward making a confident choice.
A structured approach keeps you from getting lost in the details. Instead of just comparing feature lists, begin by defining what success looks like for your organization. This often involves creating a Request for Proposal (RFP), a formal document outlining your specific needs and asking vendors how their solution meets them. Think of it as a detailed job description for your future file transfer system.
A well-structured request document ensures you gather consistent information from every vendor, making direct comparisons much easier. It forces you to define your needs for security, compliance, and functionality upfront, which is a critical exercise in itself.
To build your evaluation, focus on these core areas. Answering these questions will help you create a scorecard to compare different solutions objectively.
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, conduct a proof-of-concept (POC). This is a small-scale trial with a select group of users to test the solution in a real-world setting. A POC reveals hidden issues that datasheets and demos can’t, from integration quirks to performance bottlenecks. It’s your best chance to see if a platform truly works for your team.
Finally, when it comes to the contract, look beyond the price. Ensure the terms protect your interests. The agreement should clearly define service level agreements (SLAs), support response times, and data ownership. A good contract ensures you get not just the technology, but also the support your team needs to succeed long after implementation.
Choosing a new tool for secure online file transfer is just the starting point. The real victory comes when your team actually uses it effectively. The best technology is useless if the rollout causes chaos or everyone ignores it. The most successful launches don’t happen overnight. Instead, they begin with a focused pilot program. Think of it as a soft launch—testing the waters with a small, interested group before going all-in.
By starting with a single department or a collaborative project team, you can gather honest feedback, find unexpected quirks, and create a group of internal champions. These early adopters become your best advocates, helping train their colleagues and showing off the benefits. This step-by-step expansion, guided by real user experience, prevents the widespread disruption that often comes with big technology changes.
Even with the best plan, you’ll likely hit a few bumps. From user pushback to technical glitches, being ready for common challenges is key to keeping your rollout on track. IT leaders who’ve managed these transitions often see the same obstacles pop up.
Beyond the initial setup, long-term success requires solid operational practices. This is where governance comes in. It’s not about creating rigid rules; it’s about building a clear, sustainable framework for how the tool is used. This includes defining policies for data handling, who gets access, and how long files are kept. The shift to remote work has made secure data channels more critical than ever, driving major investments in this space. For example, one provider secured a USD 456 million funding round in August 2024 to build out its private content network. You can read more about the market forces driving these investments.
This growth shows why it’s not enough to just install a solution—you have to manage it well. A key part of this is setting up monitoring procedures. These systems help you catch problems before they affect users, making sure the platform remains a helpful asset instead of a source of frustration. By combining a thoughtful rollout with proactive governance, you ensure your investment in a secure online file transfer system actually delivers better security and productivity.
Ready to implement a solution that’s both powerful and easy to adopt? Sky Drive Folder offers robust AES-256 encryption, intuitive controls, and scalable plans perfect for a smooth transition. Explore how Sky Drive Folder can secure your file transfers today.
[…] to submit these sensitive documents, it's vital to protect your private information. Look into secure online file transfer methods to ensure your personal and medical details are kept safe. It's a simple precaution that […]
[…] Zero-Trust Security Models: The old way of thinking about security was like a castle with a moat—once you were inside, you were trusted. The zero-trust model flips this idea on its head, assuming that threats can come from anywhere, even inside your network. It works on a simple principle: "never trust, always verify." Every single request to access a document, no matter who it is or where they are, must be authenticated. While this might sound slow, modern systems use smooth, multi-factor checks that don't get in the way of legitimate users, resulting in a much stronger defense. You can find out more about putting these principles into practice with our guide on secure online file transfer. […]
There is clearly a lot to know about this. I think you made various good points in features also.
I like what you guys are up too. Such smart work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my website
I like what you guys are up too. Such smart work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my website