Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Discover our top 8 data backup best practices for 2025. Secure your global operations with proven strategies for international teams and multilingual content.
In today's interconnected world, a one-size-fits-all approach to data protection is no longer sufficient. For any individual, creative professional, or business, the loss of critical files can be devastating, leading to project delays, financial loss, or the irreversible loss of personal memories. For organisations operating across borders, the stakes are even higher. Managing multilingual content, geo-targeted landing pages, and customer data from different regions demands a sophisticated and resilient data backup strategy that acts as the cornerstone of operational continuity and growth.
This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive roundup of data backup best practices specifically tailored for modern needs. We will explore how to secure your digital assets using advanced, actionable techniques. You will learn not just what to do, but how to implement these strategies effectively, covering everything from the foundational 3-2-1 rule and automated scheduling to encryption and disaster recovery planning. For a deeper dive into the fundamentals, it's helpful to familiarise yourself with various data backup methods and best practices.
We'll examine how a platform like Sky Drive Folder, with its robust security and global accessibility, can support these practices. This guide also touches upon critical elements of an international strategy, including technical SEO for global reach and the protection of content designed for conversion optimization per region. Following these steps ensures your backups don't just protect data; they actively support your worldwide business objectives and provide peace of mind.
When establishing robust data backup best practices, the 3-2-1 rule is the universally recognized gold standard. Popularized by digital asset management expert Peter Krogh and endorsed by organizations like the US Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT), this strategy provides a simple yet powerful framework for resilience. It’s designed to protect your valuable data from nearly any single point of failure, be it a hard drive crash, software corruption, theft, or a localized disaster.
The principle is straightforward: maintain at least three total copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one of those copies offsite. This multi-layered approach ensures redundancy, insulating your critical files from isolated threats and creating a reliable recovery path.
Implementing this rule is highly adaptable for various users, from individuals to international enterprises.
For Individuals & Creatives: Your primary data (Copy 1) might live on your laptop’s internal solid-state drive (SSD). Your first backup (Copy 2) could be on an external hard disk drive (HDD) you update weekly. Your offsite backup (Copy 3) can be managed effortlessly using a cloud service like Sky Drive Folder, which automatically syncs your chosen files.
For Global Businesses: Consider a marketing agency with teams across different continents. Their original work files (Copy 1), including multilingual ad copy and geo-targeted landing pages, reside on a local server in their Toronto head office. A real-time sync to Sky Drive Folder serves as their primary backup (Copy 2), providing regional teams with fast, localized access. For ultimate disaster recovery, a third, immutable copy (Copy 3) is replicated to a separate cloud data centre in a different geographic region, like Europe, ensuring business continuity even if the primary North American infrastructure is compromised.
This infographic provides a clear summary of the core components of the 3-2-1 rule for quick reference.
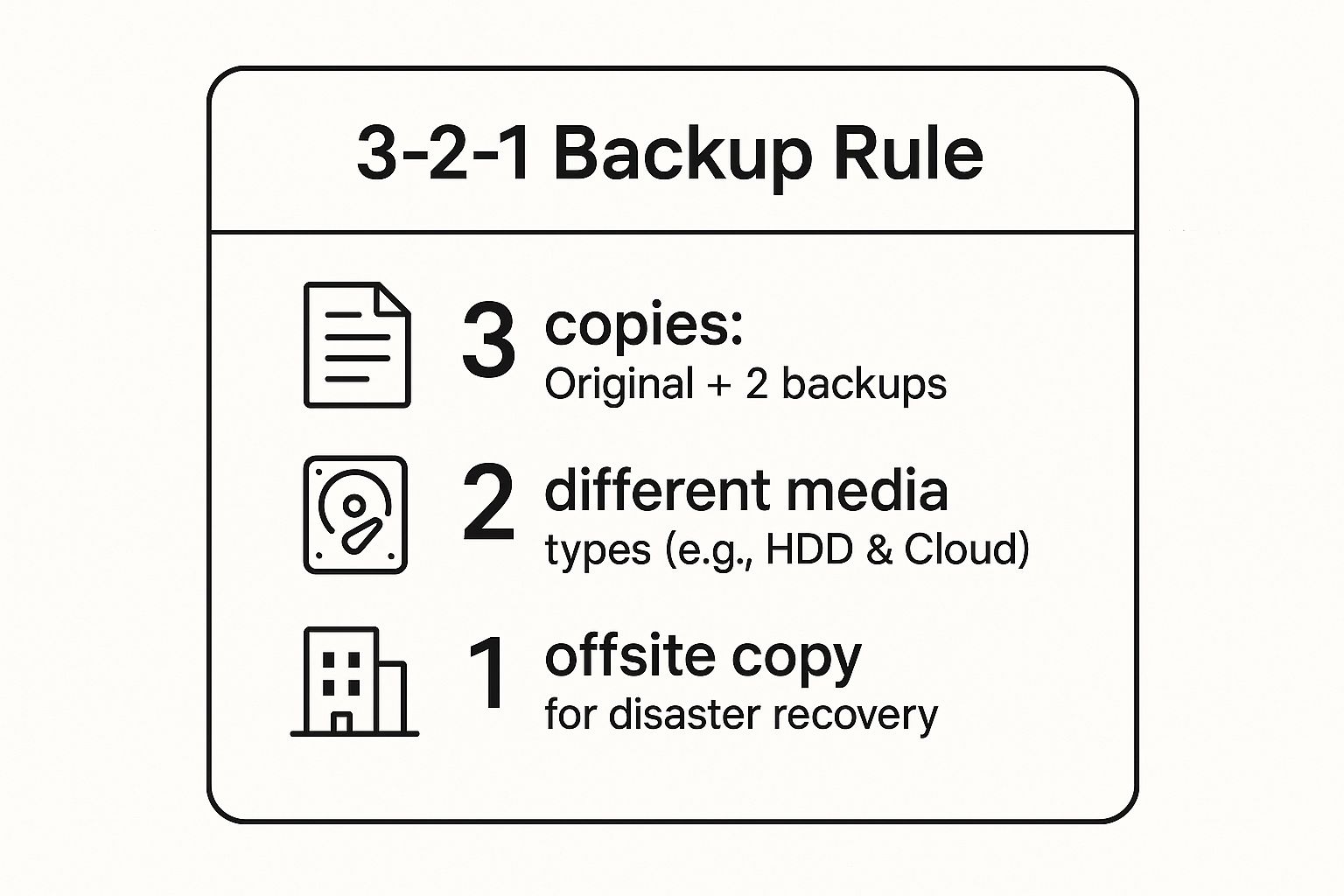
This visual breakdown emphasizes the three critical pillars of the strategy: redundancy in copies, diversity in storage media, and geographic separation for the final backup. Adhering to these simple tenets dramatically increases your data’s durability against a wide array of potential loss scenarios.
While the 3-2-1 rule provides a strategic blueprint, its effectiveness hinges on consistent execution. This is where regular automated backup scheduling becomes a cornerstone of any serious data backup best practice. Automating your backups removes the single biggest point of failure in any data protection plan: human reliance. It ensures your critical data is protected consistently at predetermined intervals without manual intervention, preventing the gaps that occur from missed or forgotten manual backups.
This practice involves configuring your backup systems, from native OS tools to sophisticated enterprise software, to run automatically. By setting a "set it and forget it" schedule, you create a dependable and predictable safety net. Modern solutions, championed by cloud providers and software vendors, can trigger backups based on time, specific data changes, or other system events, offering incredible flexibility.
Implementing an automated schedule is a critical step for ensuring data is consistently captured. The approach can be tailored to meet diverse needs, from individual users to globally distributed teams.
For Individuals & Freelancers: A freelance graphic designer can use their operating system's built-in tools, like Windows File History or macOS Time Machine, to run continuous backups of their project folders to an external drive. For offsite protection, they can configure the Sky Drive Folder desktop client to automatically sync their entire "Current Projects" folder to the cloud in real-time, ensuring every saved change is immediately backed up without a second thought.
For Global Businesses: A multinational tech firm can implement a multi-tiered automated strategy. Nightly full backups of their primary servers in their Montreal data centre are scheduled during off-peak hours to minimize performance impact. Throughout the business day, incremental backups run every hour to capture new data, including updates to their international keyword strategy documentation and multilingual content. Simultaneously, transaction log backups for their critical SQL databases might be scheduled to run every 15 minutes, ensuring the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is kept extremely low. This geo-targeted strategy ensures that teams from Europe to Asia have their contributions secured promptly.
By automating the process, organizations can focus on their core operations, confident that their data protection is running seamlessly in the background. For a deeper dive into different strategies, you can explore various small business backup solutions on blogs.skydrivefolder.com to find the right fit. This systematic approach transforms data backup from a reactive chore into a proactive, reliable, and indispensable business process.
A backup strategy is only as good as its ability to restore data successfully. This is where regular testing and verification become a cornerstone of any robust data backup best practice. Many individuals and organisations diligently back up their data, only to discover during a real crisis that the backups are corrupt, incomplete, or unusable. The practice of routinely testing backups ensures your recovery plan is functional, reliable, and capable of meeting its objectives when you need it most.
This critical step moves beyond simply checking if a backup job completed without errors. It involves actively performing restore operations to confirm data integrity and system functionality. This proactive approach, heavily promoted by disaster recovery consultants and mandated by compliance standards like PCI-DSS and SOX, is what separates a theoretical safety net from a proven one.

Integrating regular, structured testing is crucial for ensuring your data, whether personal or professional, remains recoverable. This process validates not only the data itself but also the procedures and tools used for recovery.
For Freelancers & Small Businesses: A freelance graphic designer can schedule a quarterly test. They might restore a large project folder from their Sky Drive Folder cloud backup to a secondary computer. This test verifies that their critical assets are intact and that they can quickly retrieve them to meet a client deadline, even if their primary workstation fails.
For Educational Institutions: A university with a global student body might conduct restore tests of its student information system from a Sky Drive Folder backup before the start of each semester. They would restore the database and its multilingual interface to an isolated test environment to confirm that student registrations, geo-targeted course schedules, and academic records are all recoverable without disrupting the live system, ensuring operational continuity during peak periods.
This video provides an excellent overview of why backup testing is so fundamental to data protection.
By systematically validating your backups, you build confidence in your disaster recovery capabilities. This simple, repeatable process is one of the most effective data backup best practices for transforming a backup plan from a hopeful strategy into a guaranteed recovery path.
Beyond just having a backup, one of the most critical data backup best practices involves managing which versions of your data you keep and for how long. This is where version control and retention policies come into play. This systematic approach allows you to restore files from specific points in time, not just the most recent copy. It balances storage costs against recovery needs and is essential for meeting legal and regulatory compliance obligations.
This strategy moves beyond simple data duplication to a sophisticated data lifecycle management plan. It ensures you can recover from gradual data corruption, accidental deletions, or ransomware attacks that may have gone unnoticed for days or weeks. By defining how many versions to keep and a schedule for deleting old ones, you create a powerful, historical archive of your critical information without accumulating infinite storage costs.
Implementing these policies is a strategic exercise that aligns data management with business objectives and external requirements.
For Legal and Professional Services: A law firm in Calgary must retain client files for a minimum of seven years to meet professional body requirements. Their retention policy mandates that daily backups are kept for 30 days, monthly backups for one year, and annual backups for seven years before secure deletion. This tiered approach ensures short-term recovery and long-term compliance.
For Global Software Companies: A software development company with teams in Vancouver and Berlin uses a code repository with indefinite retention for its primary intellectual property. For project files stored in their collaborative Sky Drive Folder, such as assets for various content types that drive global conversions, they implement a 90-day version history. This allows developers to roll back to any previous version from the last quarter, supporting agile development while managing storage for non-essential assets.
These policies are not just technical settings; they are fundamental business rules that govern your data's entire lifecycle. They provide a clear framework for what to save, for how long, and when it's safe to dispose of it, which is a cornerstone of responsible data governance.
Creating backups is only half the battle; ensuring they are unreadable to unauthorized parties is equally crucial. Encrypting your backup data is a non-negotiable step in modern data backup best practices, transforming your stored files into indecipherable ciphertext. This security measure protects your data both while it's being transferred (in-transit) and while it's stored on a server or drive (at-rest), serving as a powerful defence against data breaches, theft, and unauthorized surveillance.
This practice is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and is often mandated by regulatory frameworks like HIPAA and PIPEDA. For any individual or organisation handling sensitive information, encryption is the lock on your digital vault. It ensures that even if a backup medium is physically stolen or a cloud account is compromised, the underlying data remains secure and inaccessible without the correct decryption key.
Implementing robust encryption is a core feature of secure backup solutions and is vital for building trust with clients and meeting compliance obligations across different regions.
For Healthcare Providers & Legal Firms: A medical clinic in Vancouver must protect patient records to comply with British Columbia's Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA). By using a service like Sky Drive Folder, they can ensure patient data backups are encrypted both during upload and while stored in the cloud. Similarly, a law firm in Montreal can protect attorney-client privileged information, ensuring that even if a backup is intercepted, the confidential data remains secure.
For Global Financial Institutions: A Toronto-based fintech company with customers in Europe must adhere to GDPR alongside Canadian privacy laws. Encrypting all backup data is a foundational requirement. They would use end-to-end encryption for customer financial data, including that gathered from localized content on geo-targeted landing pages, ensuring it's protected from the moment it leaves their local server until it's archived in a secure, geo-targeted data centre. This multi-layered security approach is critical for their international keyword strategy and for building a trustworthy global brand.
To effectively manage this critical security layer, consider these actionable tips:
By integrating strong encryption into your backup strategy, you elevate your data protection from simple storage to a secure, compliant, and resilient archive. You can learn more about how file encryption works on blogs.skydrivefolder.com to deepen your understanding of this essential practice.
While local backups are essential for fast recoveries, they share a critical vulnerability with your primary data: physical location. A fire, flood, or theft at your office or home could wipe out both your original files and your onsite backups simultaneously. This is why incorporating offsite and cloud storage into your data backup best practices is non-negotiable for true resilience. It provides the geographic separation necessary to protect your data from localized disasters.
The strategy involves storing at least one complete backup copy in a physically separate location. This can be achieved through modern cloud services, which store your data in secure, remote data centres, or through traditional methods like sending physical media (like tapes or hard drives) to a secure third-party facility. For most users today, cloud backup offers a more automated, accessible, and scalable solution.
Implementing offsite backups is a key component of the 3-2-1 rule and can be tailored to any scale of operation, from a solo freelancer to a multinational corporation.
For Small Businesses & Freelancers: A design agency might use its local server for primary work files (Copy 1) and a network-attached storage (NAS) device for quick local backups (Copy 2). For its crucial offsite copy (Copy 3), it uses a service like Sky Drive Folder to automatically sync project folders to the cloud. This provides an affordable, set-and-forget disaster recovery solution that protects against any event affecting their physical office.
For Global Enterprises: A large corporation with offices in different countries can implement a sophisticated hybrid cloud strategy. Each regional office backs up its data to a centralized corporate data centre for operational recovery. For ultimate disaster protection, all critical data—including assets for geo-targeted landing pages and multilingual content—is then replicated to a geo-redundant cloud provider like Microsoft Azure or AWS. This approach supports technical SEO for international reach by ensuring data sovereignty and rapid recovery for any global office.
By separating your backups geographically, you build a powerful defence against catastrophic data loss. You can learn more about how to set up an effective strategy by exploring our guide to cloud backup for small business. This approach ensures that even if your primary site is completely compromised, a secure and accessible copy of your data remains safe and ready for restoration.
While full backups provide a complete snapshot, they can be time-consuming and storage-intensive. This is where incremental and differential backup strategies become essential data backup best practices. Popularized by enterprise backup software vendors like Veeam and Commvault, these methods optimize storage and speed by capturing only the data that has changed, dramatically reducing backup windows and storage costs.
This approach is centred on efficiency. An incremental backup saves only the changes made since the last backup of any type (full or incremental). A differential backup saves all changes made since the last full backup. Both methods offer a smarter way to protect data without the overhead of copying everything, every time, making them ideal for dynamic environments with frequent data modifications.
These strategies are highly effective across various scales, from individual file servers to complex virtualized infrastructures.
For Small Businesses & File Servers: A small marketing agency might use Windows Server Backup for its on-premise file server. They could schedule a full backup every Sunday night. From Monday to Saturday, they can run daily incremental backups. This means each daily backup is very small and fast, only capturing that day's new or modified client files and creative assets. Restoring requires the last full backup plus each subsequent incremental file, but the daily operational impact is minimal.
For Enterprise & Virtualized Environments: A multinational corporation using VMware for its virtual machines (VMs) can leverage these methods for immense efficiency. They might perform a full VM backup monthly. Weekly differential backups are then taken of all their digital assets, including their portfolio of localized content. If a VM needs to be restored on a Thursday, the team only needs the last monthly full backup and the most recent weekly differential backup. This simplifies the restore process compared to a long incremental chain while still saving significant space over daily full backups.
Choosing between incremental and differential depends on your recovery time objectives (RTOs) and storage capacity. Incremental is faster and uses less space daily, but restoration can be more complex. Differential uses more space over time but offers a simpler, quicker restore process, a critical consideration for your disaster recovery procedures.
Advanced data backup best practices are not just about technology; they are equally about process and preparation. A comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) with detailed documentation is the critical playbook that transforms a well-designed backup system from a passive asset into an actionable recovery solution. Without it, even the most robust backups can fail during a crisis due to confusion, missing information, or procedural errors.
This plan is a formal, documented set of policies and procedures to recover or continue vital technology infrastructure and systems following a disaster. It ensures that in a high-stress situation, your team can act decisively and correctly, minimizing downtime and data loss. This organised approach is a hallmark of mature business continuity management, mandated by compliance frameworks like HIPAA and PCI-DSS.
Creating a DRP involves a thorough analysis of potential threats and a step-by-step guide for every conceivable recovery scenario.
For E-commerce Companies: A retailer’s DRP would include detailed procedures for restoring its online storefront and all its geo-targeted landing pages. This includes steps for recovering the product database from a Sky Drive Folder backup, re-establishing payment gateway connections, and bringing customer relationship management (CRM) systems back online. The documentation would have contact lists for service providers and assigned roles for the technical team to ensure a swift, coordinated response.
For Healthcare Systems: A hospital must maintain rigorous documentation for patient data recovery to comply with privacy laws. Their plan would outline the precise sequence for restoring electronic health records (EHR) from secure, encrypted backups. It would specify who has the authority to initiate recovery, how to verify data integrity post-restoration, and communication protocols for informing staff and regulatory bodies, ensuring patient care and legal obligations are met. For advanced planning and leveraging modern infrastructure, consider exploring comprehensive estrategias de DRP en la nube to integrate cloud-native resilience.
A well-documented plan is a living document, not a file you create once and forget. It must be tested, updated, and accessible when needed most. It should also include plans for rebuilding digital assets like your backlink profile in target regions, a crucial step for restoring online authority after a major outage. This ensures your recovery roadmap remains relevant and effective, turning potential chaos into a controlled, predictable process.
| Strategy / Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-2-1 Backup Rule | Moderate (requires multi-location setup) | High (multiple storage media and sites) | Robust data protection against diverse failures | Personal to enterprise data protection | Clear minimum standards, multi-layered safety |
| Regular Automated Backup Scheduling | Low to Moderate (initial setup + maintenance) | Medium (automation tools, monitoring) | Consistent, timely backups without human error | Any environment needing reliable backup frequency | Eliminates human error, reduces admin overhead |
| Regular Backup Testing & Verification | Moderate to High (test systems and procedures) | Medium to High (test infra, time) | Verified restore capabilities and data integrity | Critical systems where restore confidence is vital | Detects failures early, boosts recovery confidence |
| Version Control and Retention Policies | High (policy design and management) | Medium to High (storage for versions) | Efficient storage use with legal/regulatory compliance | Regulatory-heavy industries, long-term data retention | Balances cost and compliance, multiple recovery points |
| Encryption of Backup Data | Moderate (key management and integration) | Medium (encryption tools, key storage) | Secure backups preventing unauthorized access | Sensitive data environments requiring confidentiality | Strong security, compliance with data protection |
| Offsite and Cloud Backup Storage | Moderate (cloud setup and integration) | Medium to High (cloud subscription, bandwidth) | Disaster recovery through geographic diversity | Protection from local disasters, scalable storage | Scalability, disaster recovery readiness |
| Incremental & Differential Backups | High (complex backup software and management) | Medium (software and monitoring) | Faster backups, reduced storage use | Large data sets, frequent backup needs | Efficiency in speed/storage, frequent backups |
| Documentation & Disaster Recovery Planning | High (detailed documentation and updates) | Low to Medium (time and coordination) | Faster, consistent recoveries during disasters | Organizations needing regulatory compliance and business continuity | Reduces recovery time, ensures accountability |
The journey through these essential data backup best practices reveals a fundamental truth: robust data protection is no longer a passive background task. It has evolved into a dynamic, strategic pillar that underpins organizational resilience, operational agility, and global competitiveness. Moving beyond mere data recovery, the goal is to achieve true business continuity, ensuring your operations remain stable and trustworthy, regardless of unforeseen disruptions.
Mastering these principles transforms your approach from reactive to proactive. You are no longer just saving files; you are architecting a resilient future for your data. The core concepts we've explored, such as the 3-2-1 Rule, automated scheduling, and rigorous backup testing, form the unshakable foundation of this architecture. These aren't just technical checkboxes; they are strategic manoeuvres that guarantee data availability and integrity when it matters most.
A modern data protection strategy must extend beyond your local server room. In today's interconnected world, your data's reach is global, and so your backup strategy must be too. This is where advanced concepts like international keyword strategies and multilingual content considerations intersect with data backup. Imagine a scenario where a regional marketing campaign's localized assets are lost. A generic backup might restore the files, but a globally-aware strategy ensures you recover the correct, geo-targeted versions, preserving your market-specific messaging and investment.
This forward-thinking approach involves integrating several key global elements into your disaster recovery plan:
By viewing your backup system through this global lens, you are not just protecting data; you are safeguarding your international market presence.
Ultimately, adopting these data backup best practices is about building an unbreakable organisation. It’s about instilling confidence in your team, your partners, and your customers across every region you serve. When you can guarantee that data is secure, versioned correctly, and rapidly recoverable, you create a stable platform for innovation and growth. You free your team from the fear of digital catastrophe, allowing them to focus on driving value and expanding your global footprint.
A comprehensive platform like Sky Drive Folder becomes the linchpin in this strategy. It provides the secure, scalable, and globally accessible infrastructure needed to implement these advanced practices, from encrypted offsite storage to seamless collaboration for remote international teams. The ultimate objective is clear: to ensure that no matter what challenge arises, from a simple hardware failure to a significant cyber-attack, your business doesn't just survive, it thrives. This is the new standard for excellence in a data-driven world.
Ready to implement these data backup best practices with a platform built for security and global accessibility? Sky Drive Folder offers the robust tools you need, from automated backups and versioning to encrypted cloud storage, all in one intuitive solution. Protect your digital assets and secure your future by exploring Sky Drive Folder today.
[…] protected. An insightful article that delves into best practices for data backup can be found here. This resource provides valuable tips on how to maintain the integrity and accessibility of your […]