Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Master HIPAA compliant file sharing with our guide. Learn to select tools, configure security, and train staff to protect patient data and ensure compliance.
HIPAA-compliant file sharing isn't just a US-centric technical term; it’s the practice of using specific technologies and rules to send sensitive electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) without breaking strict regulatory standards. And while it originates in the US, its core principles of encryption, access control, and auditability have become the global gold standard for protecting patient data, crucial for any organization with an international footprint. This guide addresses the complexities of maintaining compliance across different regions and languages.

In our interconnected world, protecting patient data is a responsibility that knows no borders. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) might be a United States law, but its security framework provides a powerful blueprint for healthcare organisations everywhere, from those in the UK navigating GDPR to clinics in Asia handling international patient records. Following these standards is no longer just about ticking a compliance box; it's about earning patient trust and ensuring care continues smoothly in a digital-first, globalized world.
The stakes are unbelievably high. Healthcare providers are a prime target for cyberattacks because of the incredibly valuable data they hold. This isn't some far-off possibility; it's a real and immediate danger threatening both patient safety and the stability of healthcare organisations, regardless of their location.
The explosion in cyber threats aimed at the healthcare sector makes it painfully clear why we need secure file-sharing solutions with an international reach. Globally, healthcare has suffered 1,710 security incidents with 1,542 confirmed data disclosures, many of which were caused by ransomware and espionage. This isn't just a US problem; we see the same pattern in Europe, where health providers face a growing number of attacks that expose sensitive patient data, often violating regional data sovereignty laws.
This new reality makes casual file-sharing methods—like standard email or your personal cloud storage account—dangerously obsolete. Sending an unencrypted file with patient test results or personal details is like mailing a postcard with sensitive medical information scrawled on the back for anyone to see, regardless of the language it's written in.
A single breach can be catastrophic. It can lead to massive financial penalties under multiple jurisdictions (e.g., HIPAA and GDPR) and cause irreparable damage to a provider's reputation. Worse, it can disrupt patient care and shatter the trust that is the very foundation of the patient-caregiver relationship.
To properly defend against these threats, your organization needs a defence with multiple layers. True HIPAA-compliant file sharing is built on several fundamental security measures that work together to shield electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) every step of the way, forming a foundation for global data protection strategies.
Here are the key security measures you can't do without:
Ultimately, these security pillars are about more than just technology; they are essential to modern risk management and patient care. For a closer look at the specific requirements, you can explore resources on secure HIPAA compliant document sharing. Once you understand these core concepts, you can better appreciate why building a resilient security posture is so important. You can also read our guide on the best practices for secure file sharing to get started.
Picking the right technology for HIPAA compliant file sharing is where all your security planning meets reality, especially when operating internationally. This isn't just about ticking boxes on a vendor's feature list; it’s about finding a genuine partner in protecting patient data across borders. You need a practical way to weigh your options, considering technical SEO aspects like hreflang tags for multilingual portals and the ability to create geo-targeted landing pages for different regional compliance needs.
The absolute first step—and this is non-negotiable—is the Business Associate Agreement (BAA). Don't mistake this for a simple formality. It's a legally binding contract that holds your vendor accountable for protecting ePHI. If there's a breach on their end, that BAA is what makes them legally responsible. When you're looking at potential services, your first question should be whether they will sign formal Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) or BAAs, which are crucial for both HIPAA and GDPR compliance. If the answer is no, walk away.
A signed BAA is essential, but it’s just the starting point. The platform itself needs a strong set of built-in security features to guard sensitive information against threats, both from the outside world and from within your organization. A BAA is meaningless if the technology backing it is weak.
As you evaluate your options, your checklist has to prioritize these core features:
These features aren't nice-to-haves; they are the fundamental pillars of any truly secure system. For a deeper dive into these technical requirements, our a guide to HIPAA compliant cloud storage is a great resource.
The infographic below shows how these elements come together in a continuous cycle.
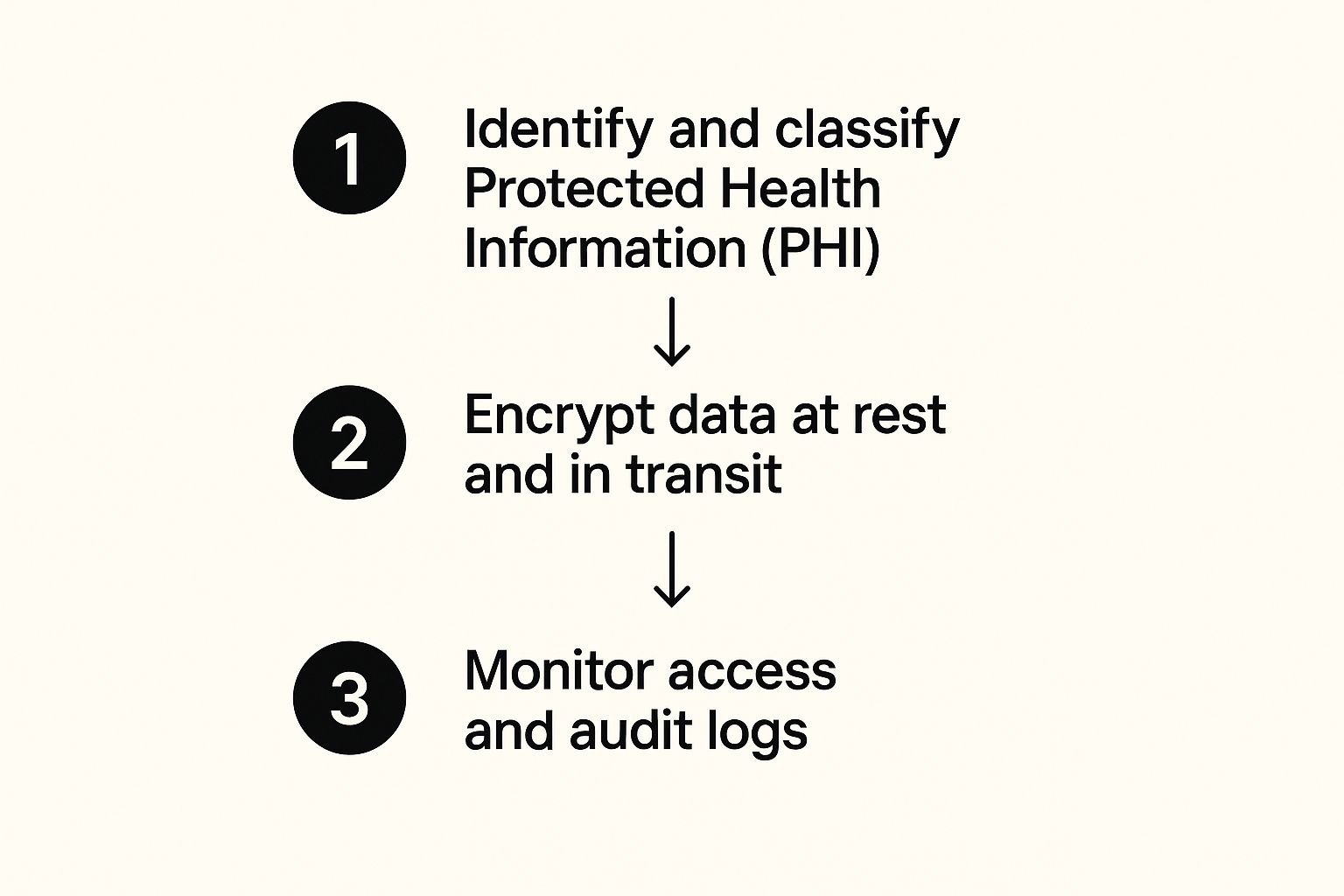
As you can see, solid data protection is never a "set it and forget it" task. It's a constant process of classifying your data, ensuring it's encrypted, and keeping an eye on who is doing what with it.
To make it even clearer, here’s a breakdown of the must-have features and why they are so critical in day-to-day healthcare operations, regardless of location.
| Feature | Why It's Critical for Compliance | Example in Practice |
|---|---|---|
| End-to-End Encryption | Protects ePHI from being intercepted or read by unauthorized parties, both during transfer and while stored. | A clinic in Germany sends patient lab results to a specialist in the US. Encryption ensures the data is unreadable even if intercepted over international networks. |
| Business Associate Agreement (BAA) | A legally required contract that obligates your vendor to uphold HIPAA security standards, making them liable for breaches. | Your practice signs a BAA with a cloud storage provider, legally binding them to protect the patient records you store on their platform, regardless of patient nationality. |
| Granular Access Controls | Enforces the "minimum necessary" rule by restricting user access to only the specific data they need for their job role. | A billing clerk in your Manila office can only view insurance information, while a physician in London has access to the full patient medical history. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds a vital layer of security to prevent unauthorized access, even if a user's password has been stolen. | To log in, a nurse must enter their password and then a unique code sent to their mobile phone, stopping a hacker with a stolen password from anywhere in the world. |
| Detailed Audit Trails | Provides a complete, unchangeable record of all activity, which is essential for investigating incidents and proving compliance during an audit. | An administrator can instantly pull a report showing exactly who viewed a specific patient's file in the last 30 days, including timestamps and IP addresses. |
Ultimately, a truly compliant solution integrates these features seamlessly, making security an enabler of efficient work, not a barrier to it. This includes considering conversion optimization per region; for instance, ensuring the user interface is intuitive for multilingual teams.
Let’s bring this down to earth. Imagine a busy staff member accidentally tries to share a patient’s entire medical record with a research partner in another country instead of the anonymized dataset they were supposed to send. It's an honest mistake, but one with huge consequences. With granular permissions, you can configure the system to outright block any folder tagged "Full ePHI" from being shared with an external email address, stopping the error before it can even happen.
Here's another one: you suspect that certain patient records were viewed improperly from an unfamiliar IP address abroad. Instead of a drawn-out, panic-filled investigation, comprehensive audit logs let you know in minutes. An administrator can immediately see which user accounts accessed the files, from what IP addresses, and at precisely what times. This kind of rapid response capability is absolutely critical.
Choosing the right platform is about more than just checking off compliance boxes. It’s about mitigating risk at every possible turn by finding a service that not only promises security but gives you the practical, tangible tools you need to enforce it every single day, across every region you operate in.

A platform that supports HIPAA compliant file sharing is only as strong as its setup. An out-of-the-box configuration is almost never enough; you have to actively fine-tune the security settings to create a genuinely sealed environment for electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). Simply having the right tools is just the start—how you use them is what truly defines your security posture in the real world.
Misconfigurations are a massive, yet often overlooked, cause of data exposure. In fact, one report revealed that poorly configured cloud infrastructure was to blame for exposing nearly 70% of compromised records. That stark figure shows that human error and sloppy setup are often bigger vulnerabilities than malicious attacks. Locking down your system should be your absolute first priority.
The Principle of Least Privilege is a beautifully simple concept: give users the absolute minimum level of access they need to do their jobs, and nothing more. This single strategy dramatically cuts down the risk of both accidental and intentional data misuse, a core tenet of both HIPAA and GDPR.
To put this into practice, you need to get surgical with user roles and permissions. Forget about using generic, one-size-fits-all access levels. Instead, it’s all about creating custom roles based on specific job functions, which might vary by region.
By organizing permissions this way, you ensure that if an account is ever compromised, the potential damage is contained to that user's very narrow scope of access.
Beyond user roles, several other security settings are non-negotiable for locking down your system. Think of them as layers that work together to create a formidable defence against unwanted access.
First up, enforce a strong password policy. This isn't just about length; it needs to demand complexity (a mix of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols) and be rotated regularly.
Next, you absolutely must activate multi-factor authentication (MFA) across the board. A password alone just doesn’t cut it anymore. MFA requires a second form of verification, like a code sent to a mobile phone, making it significantly harder for an attacker to get in, even if they’ve stolen a user's password.
Setting automatic session timeouts is another crucial, yet often overlooked, security measure. This automatically logs users out after a set period of inactivity, preventing unauthorized access from an unattended, logged-in workstation.
Finally, your security configuration has to address the full data lifecycle, which includes its eventual disposal. Holding onto patient data indefinitely not only creates unnecessary risk but can also clash with data minimisation principles found in both HIPAA and GDPR.
You need to establish and automate a clear data retention and disposal schedule. Work with your legal and compliance teams to figure out exactly how long different types of ePHI must be kept, which may vary by country. Once that period is up, the data should be securely and permanently wiped. This not only shrinks your risk surface but also helps you stay compliant with various international regulations.
You can get a deeper understanding of these practices in our comprehensive guide on how to share files securely. By taking these configuration steps, you transform a compliant platform into a true fortress for patient data.
You can have the most advanced security tech in the world, but it can all be undone by a single, uninformed click. While secure platforms and careful configurations are critical for HIPAA-compliant file sharing, it’s your team that stands on the true front line of defence. The goal isn't just to avoid mistakes; it's to turn your staff from a potential weak link into a robust human firewall, especially when dealing with multilingual teams and localized content.
Technology gives you the locks, but it’s people who hold the keys. What you’re really trying to build is a security-first mindset, where every person instinctively understands their role in protecting sensitive patient data. This all starts with clear, accessible, and potentially multilingual policies that people can actually use.
It’s no secret that healthcare is a major target. The latest data shows a staggering 239% increase in hacking incidents targeting the sector between 2018 and 2023. For global organizations navigating both HIPAA and GDPR, this makes airtight file-sharing methods more urgent than ever. A compliant solution has to weave together encryption, strict access controls, and full audit trails to meet the overlapping demands of HIPAA, GDPR, and other regional data protection acts.
Vague guidelines are worse than useless in a real-world scenario. Your file-sharing policies need to be direct, easy to digest, and leave zero room for guesswork. For international teams, this means creating localized content—translating policies and training materials to ensure clarity and comprehension across different languages and cultures.
Your policies should spell out the answers to these critical questions in plain English:
When you create straightforward, localized rules, you give your team the confidence to make the right call every single time. For more on this, our guide to secure document sharing offers some great best practices.
A single annual training session is a box-ticking exercise that’s quickly forgotten. If you want to build a lasting security-first culture, training has to be an ongoing, engaging process that reinforces good habits all year round.
The most effective training moves beyond abstract rules and immerses staff in real-world situations. It’s about building muscle memory so that spotting a threat becomes second nature.
Your training program should be a dynamic mix of different formats to keep people engaged. Consider a strategy that includes different content types that drive global conversions and comprehension:
1. Regular Phishing Simulations
Send out simulated phishing emails that look just like the real attacks targeting healthcare. These tests give staff a safe space to fail, learn, and sharpen their ability to spot a malicious attempt. Use the results to see who might need a bit of extra coaching.
2. Scenario-Based Workshops
Forget boring lectures. Present your teams with realistic situations, perhaps localized to their region. For example: "A partner organization in the EU emails you asking for a patient list for a research project, but they aren't on our approved vendor list. What are the GDPR and HIPAA implications?" Talking through these scenarios as a group helps solidify the correct procedures in a way a PowerPoint slide never could.
3. Bite-Sized Security Updates
Use your internal newsletter or team meetings to share brief "security tips of the week" in multiple languages. You could highlight a new type of scam doing the rounds, offer a quick reminder about password hygiene, or even share a success story where an employee correctly spotted and reported a threat.
This continuous approach transforms training from a chore into a core part of your company culture, ensuring your human firewall gets stronger and more resilient over time.

Getting compliant isn't a one-and-done project; it’s a continuous commitment. For any organization serious about HIPAA compliant file sharing, especially those with international operations, the real work starts after you’ve got everything set up. It’s this ongoing vigilance that separates a genuinely secure environment from one that just has the right tools.
You have to constantly monitor, audit, and refine your processes. Security threats are always evolving, human error is inevitable, and even the best policies can drift over time. Without regular checks, the most robust system can develop weak spots, leaving sensitive patient data dangerously exposed across different jurisdictions.
Your chosen file-sharing platform should be your best friend here, offering a goldmine of data through its audit logs and reporting features. These tools are your first line of defence in maintaining compliance. They give you an unchangeable record of every single action taken within your system, opening a clear window into user behavior.
Regularly reviewing these logs isn't just a "best practice"—it's an operational necessity. You should be actively hunting for unusual activity that might signal a problem. This proactive approach lets you spot potential issues before they spiral into full-blown incidents.
Keep an eye out for these key activities:
By making log reviews a routine part of your security protocol, you shift from being reactive to proactive.
Think of audit logs as your system's security camera footage. You don't just review it after a break-in; you monitor it consistently to deter threats and spot suspicious behaviour as it happens.
While daily log reviews are great for spotting immediate threats, periodic internal audits give you a much broader view of your compliance health. These are structured, deep dives into your entire file-sharing ecosystem. A comprehensive guide to IT compliance standards can simplify this process by outlining exactly what regulators expect to see.
An internal audit needs to be a systematic check-up, not a random search. Here’s a practical checklist to guide your efforts:
These audits should be done at least once a year—more often if you're a larger organization. The goal is simple: find and fix vulnerabilities before an external auditor does.
No matter how strong your defences are, you have to prepare for the worst. A documented incident response plan is a non-negotiable part of HIPAA compliant file sharing. When a potential breach happens, a clear plan prevents panic and enables a swift, organized response to minimize the damage.
Your incident response plan is your playbook for a crisis, outlining clear steps for everyone to follow.
Key Stages of an Incident Response Plan:
For more on this, our article on secure online file transfer offers additional insights into building a truly resilient security framework. Ultimately, maintaining compliance is a cycle of monitoring, auditing, and preparing—ensuring your data protection efforts stay effective day in and day out.
When it comes to HIPAA-compliant file sharing, it’s natural to have a lot of questions. Healthcare professionals and IT admins are often caught between local rules and global data standards, trying to find a system that’s both compliant and actually usable for daily work. Getting clear, practical answers is the only way to build a security framework that doesn’t get in the way.
Here are some of the most common questions we hear, with straightforward answers to help you sidestep the big compliance traps.
The short answer is a hard no. Standard email is fundamentally insecure for sending electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). Most email services you use every day lack the end-to-end encryption needed to shield data as it zips across the internet. It's the digital equivalent of mailing sensitive medical records on a postcard for anyone to read.
True HIPAA-compliant file sharing demands a secure, encrypted platform that keeps a complete, auditable log of every file transfer. On top of that, compliance requires you to have a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with your service provider—a legal contract that standard email platforms simply don't offer. Using a dedicated, secure solution is the only real way to tick all these boxes.
A Business Associate Agreement (BAA) is a legally binding contract between a healthcare provider (the "covered entity") and any third-party service they use, like a file-sharing platform (the "business associate"). This agreement is an absolute cornerstone of HIPAA compliance.
The BAA legally obligates the vendor to protect any ePHI they handle with the same rigour as the healthcare provider. It outlines their responsibility for safeguarding patient data and defines their liability if a data breach occurs.
For any organization, especially one with international clients, a BAA is non-negotiable due diligence. It formally documents your vendor’s security promises, which aligns nicely with the principles of other data protection laws like GDPR, where it is often referred to as a Data Processing Agreement (DPA). Operating without one for any service that touches ePHI is a serious compliance violation.
While HIPAA is a US healthcare law and GDPR is the main data protection regulation for the EU and UK, they’re built on many of the same core ideas. This overlap is crucial for any organization with a global footprint.
Both frameworks demand:
Because they share these foundations, a platform designed to meet HIPAA's tough technical standards is often an excellent starting point for GDPR compliance. The key is to make sure your chosen solution and your internal policies are flexible enough to handle the specific details of every regulation you need to follow, including data sovereignty requirements.
One of the most common—and dangerous—mistakes is assuming a platform advertised as "HIPAA compliant" is secure right out of the box. True compliance isn't a feature you buy; it's an active process you have to manage.
Failing to properly configure the system leaves massive security holes. This often means neglecting to:
Another critical error is forgetting to sign a Business Associate Agreement with your vendor. Using popular services like Dropbox or Google Drive without their specific business-tier plans and a signed BAA is not compliant. This oversight leaves your organization exposed to serious legal and financial penalties because there's no legal contract holding the vendor accountable for protecting your patients' data.
Ready to secure your data with a truly compliant solution? Sky Drive Folder offers robust AES-256 encryption, customisable access controls, and detailed audit logs to support your HIPAA and global compliance needs. Simplify your secure file management by visiting https://skydrivefolder.com to see how our platform can protect your organization.
[…] in the United States set an even higher standard. Understanding how encryption forms the bedrock of HIPAA-compliant file sharing is crucial for any business in that space. This dedication to security and regulation shows […]