Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Discover essential cloud data protection strategies to secure your assets. Learn best practices for encryption, compliance, and disaster recovery.
Moving your business to the cloud gives you incredible flexibility, but it can also lull you into a false sense of security. Cloud data protection isn't just about having your data on the cloud; it's the practice of actively securing it in the cloud. This is a responsibility that falls squarely on your shoulders, not just your provider's. It’s all about putting the right strategies and tools in place to shield your information from breaches, loss, and prying eyes.
Shifting to the cloud is a bit like leasing a space in a high-security building. The landlord—your cloud provider—gives you a vault with thick steel walls and a state-of-the-art alarm system. That’s them securing the physical infrastructure.
But you’re the one who has to set the combination lock. You decide who gets a key, and you’re responsible for making sure the vault door is actually shut and locked. Believing the landlord is handling all of that for you is a critical, and common, mistake.
This idea of shared duties is a core concept in the cloud. Providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are responsible for the security of the cloud—their global network, their hardware, their data centres. But you are responsible for security in the cloud. That means protecting your data, your applications, and how your users are configured to access everything.
The Shared Responsibility Model is the official rulebook that divides up these duties. Your provider secures the "cloud," but you secure what you put inside it. If you neglect your side of the bargain, you’re leaving the door wide open for trouble.
For instance, your provider makes sure no one can break into their server rooms. But they can’t stop one of your employees from accidentally making a folder of sensitive client files public. That's where your own cloud data protection strategy kicks in, governing how data is handled, who can touch it, and how it’s moved. This includes everything from managing user permissions to ensuring you use a secure online file transfer method for sensitive documents.
Ignoring your role in cloud security isn't a risk; it's a guarantee of future problems. The threats are very real: data breaches that make headlines, operational downtime that grinds your business to a halt, and eye-watering fines for compliance failures. These aren't just hypotheticals—they happen to organisations of all sizes, every single day.
The hard truth is that cyber threats are a constant, growing problem. In the United Kingdom, just over 40% of businesses reported some form of cyber security breach or attack in the last 12 months.
What’s even more alarming is that 45% of data leaks involve cloud environments. When a breach spans multiple systems, it can take an average of 283 days just to spot and contain it, all while the financial and operational damage piles up. You can dig into more cloud security threats on techmagic.co to see the full picture.
Failing to build a proper cloud data protection plan leaves your organisation dangerously exposed. The fallout can range from devastating financial losses and a shattered reputation to severe penalties from regulators. Proactive protection is no longer a "nice-to-have"—it's a fundamental cost of doing business in the modern world.

To really protect your data in the cloud, you need more than just a single tool or a fancy firewall. True cloud data protection is a strategy built on a few core pillars. Each one defends against a different kind of threat, and when they work together, they form a seriously tough defence for your most important digital assets.
Think of it like securing a house. You wouldn't just lock the front door and call it a day. You'd also check the windows, install an alarm, and maybe keep your most valuable items in a safe. The same logic applies here—your cloud security needs layers.
The first and arguably most important pillar is Identity and Access Management (IAM). This is your digital bouncer, deciding who gets into your cloud environment and what they’re allowed to touch once they’re inside. Without solid IAM, all your other security efforts can be easily sidestepped.
Imagine giving every single employee a master key that unlocks every door in the office—from the broom closet to the CEO’s office and the server room. It would be an absolute nightmare. IAM prevents this by assigning permissions based on roles and responsibilities. Your marketing team can get into the campaign folders, but they have no business accessing sensitive financial records or critical system settings.
This is all built on the principle of ‘least privilege’—a simple but powerful idea. You give people the absolute minimum level of access they need to do their jobs, and not a drop more. This dramatically shrinks your attack surface. If an employee’s account gets compromised, the damage is contained to only what that user could access, not your entire system.
A non-negotiable part of modern IAM is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). By requiring a second proof of identity, like a code from a mobile app, you make it incredibly difficult for an attacker to get in, even if they’ve stolen a password. It's one of the single most effective security moves you can make.
Next up is data encryption, which is essentially a secret code for your information. It works by scrambling your data into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered with the correct key. This protection is critical in two states: when your data is sitting still and when it's on the move.
With proper encryption, your data stays private and secure even if it’s intercepted or the storage itself is breached. For businesses that need to share sensitive files, combining strong encryption with other controls is crucial. You can dive deeper into this by exploring strategies for https://blogs.skydrivefolder.com/secure-document-sharing that balance robust security with practical usability.
The final pillar is your ultimate safety net: backup and disaster recovery (DR). Let's be realistic—no matter how strong your defences are, things can still go wrong. A system can fail, a human error can corrupt data, or a ransomware attack could lock you out of your own files.
A backup is just a copy of your data, stored somewhere safe and separate. If your primary data gets wiped out, you can simply restore it from this copy. Disaster recovery is the bigger picture—it's your complete playbook for getting the entire business back on its feet after a major incident. This plan covers not just restoring data, but also the servers, applications, and networks you need to keep operating.
As you lay down your security foundation, it's vital to know where your weak spots are. Using a good cybersecurity risk assessment template can help you spot and fix potential threats before they turn into full-blown disasters. Skipping any of these foundational pillars is like building a house on a shaky foundation; sooner or later, it’s going to collapse.

Even the most powerful cloud data protection tools are useless if they aren’t set up correctly. The uncomfortable truth is that the single biggest cause of cloud security incidents isn’t a shadowy hacker group or a flaw in the provider’s hardware; it’s simple human error. One small oversight in configuration can leave a massive, gaping hole in your defences.
Think of it like this: you've installed a top-of-the-line security system in your home, complete with reinforced doors and unbreakable windows. But if you leave a key under the doormat, none of that matters. A simple mistake has bypassed all your sophisticated protections. This is exactly what happens in the cloud when settings are misconfigured.
These errors aren’t complex hacks; they are basic slip-ups. An engineer might accidentally leave a storage bucket with sensitive customer data open to the public internet. Another might grant an application far more permissions than it needs, turning it into a potential backdoor. These small, preventable mistakes are the digital equivalent of leaving the key under the mat, and they are frighteningly common.
Some misconfigurations are more dangerous than others because they are both common and create easy opportunities for attackers. These digital "open doors" are often the first things cybercriminals look for when probing a target's cloud environment.
These simple errors are the root cause of many high-profile data breaches. The scale of the problem is significant; it is estimated that nearly 23% of cloud security incidents come from misconfiguration errors, making it the third most common attack vector. In the UK, 27% of businesses report experiencing public cloud security breaches caused by these kinds of missteps. You can explore more about these findings and what they mean for businesses in this detailed cloud security report on bluefire-redteam.com.
It's one thing to talk about these errors in theory, but seeing them in a real-world context makes the risk much clearer. Here's a look at some frequent mistakes and, more importantly, how to avoid them.
| Misconfiguration | Potential Impact | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Public S3 Buckets | Massive data exposure of sensitive customer or company files, leading to regulatory fines and reputational damage. | Implement automated tools that continuously scan for and alert on publicly accessible buckets. Use bucket policies to explicitly deny public access by default. |
| Overly Permissive IAM Roles | A compromised account or service can lead to a full environment takeover, data theft, or service disruption. | Enforce the principle of 'least privilege'. Only grant the minimum permissions necessary for a user or service to function. Regularly audit roles and remove unused permissions. |
| Unrestricted Outbound Traffic | Malware on a compromised instance can "phone home" to an attacker's server, exfiltrating data or receiving further commands. | Configure security groups and network ACLs to block all outbound traffic by default. Only allow connections to specific, trusted IP addresses and ports as needed. |
| Missing Encryption | Data stored in databases or storage services can be read by anyone who gains access if it's not encrypted at rest. | Enable encryption by default on all storage services (like EBS, S3, RDS). Use services like AWS KMS to manage encryption keys securely. |
| Hard-coded Secrets in Code | Developers expose API keys, database passwords, and other credentials when code is pushed to public repositories. | Never hard-code secrets. Use a dedicated secrets management service (like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault) to store and retrieve credentials at runtime. |
As the table shows, a proactive and automated approach is your best defence. Relying on manual checks alone is a recipe for failure in complex cloud environments.
The good news is that these disasters are entirely preventable with the right processes and tools. Strengthening your cloud data protection strategy isn't about buying more software; it's about establishing a culture of security and implementing smart, automated checks.
Start by strictly enforcing the principle of 'least privilege'. No user or service should have more access than is absolutely necessary to perform its function. This simple discipline contains the potential damage from a compromised account. It’s a foundational concept of good security hygiene.
Next, you must use automated tools to continuously scan your environment for misconfigurations. Cloud providers offer their own security posture management services, and many third-party tools are also available. These solutions act as a constant watchdog, alerting you the moment a storage bucket is made public or an insecure setting is detected.
Regular security audits are non-negotiable. Think of them as routine check-ups for your cloud environment. These audits, whether performed internally or by an external firm, help you find and fix vulnerabilities before an attacker can exploit them. They provide a clear, objective view of your security posture.
Ultimately, avoiding these disasters comes down to diligence. By combining strict access controls, automated scanning, and regular audits, you can catch human errors before they escalate into catastrophic breaches. It's how you find and remove the "key under the doormat," ensuring your sophisticated defences can do their job properly.

Operating in a connected world means your data doesn’t just stay in one place; it travels across borders. This international reach brings enormous opportunity, but it also throws a complex web of data protection regulations in your path. A solid cloud data protection strategy has to go beyond technical security and tackle global compliance head-on. This is a core part of any successful international keyword strategy, ensuring your digital presence is both secure and legally sound in every market you enter.
Think of it like international shipping. You can’t just send a package anywhere without thinking about the customs laws, taxes, and restricted items for each country. Data is no different. Failing to respect these digital borders can lead to severe consequences, including fines that can cripple a growing business.
Two critical concepts you absolutely must get your head around are data residency and data sovereignty. They sound similar, but they address different aspects of how your data is governed.
Data residency is pretty straightforward: it’s the physical, geographical location where your data is stored. If you’re a UK business serving local customers, for example, data residency rules might require their personal information to stay on servers located within the United Kingdom.
Data sovereignty is a bigger legal idea. It means that your data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it’s physically located. So, if your data is sitting on a server in Germany, it falls under German and EU laws, including the tough requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Understanding this distinction is vital. It’s not just about where your data lives, but whose rules it lives by. A good cloud data protection plan must account for both to ensure you remain compliant across all your markets.
Your cloud provider is a key partner in all of this. Leading providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have massive global infrastructure, which allows you to choose the specific region where you want to store and process your data. This is your number one tool for managing data residency and a key component of your technical SEO for international reach.
But remember the Shared Responsibility Model. The provider gives you the tools to select a data centre in London or Dublin, but it's your job to configure your applications to use them correctly. The provider won't stop you from accidentally replicating UK customer data to a server in the US; that control is on you. For smaller companies, getting these settings right is a core part of their cloud backup for small business strategy, as it protects them from both data loss and regulatory penalties.
The GDPR is the perfect example of a regulation with a global punch. It protects the data of EU citizens, which means that even if your business is based in the UK, you must comply with its rules if you handle data belonging to people inside the EU. For those navigating the complexities of international regulations, understanding specific frameworks is paramount for robust cloud data protection, and there are many helpful resources that offer clear GDPR compliance information to guide your efforts.
Achieving compliance isn't just about clearing a legal hurdle; it's a mark of trustworthiness that shows customers you take their privacy seriously. This trust is essential for conversion optimization per region, as customers are more likely to engage with businesses that respect their data rights. By using your cloud provider's tools to control where your data lives and who can access it, you can build a secure and legally sound operation that's ready to serve customers anywhere in the world.
Knowing the theory is one thing, but putting it into practice is where the real work begins. A solid cloud data protection framework isn't something you can guess at; it's built step-by-step with a clear, deliberate strategy. Think of it as building a house—you need a solid foundation before you can put up the walls. This action plan will walk you through the four critical phases you need to build a resilient security posture for your organisation.
You can't protect what you don't know you have. It's a simple truth, but one that many organisations overlook. The very first step is a thorough discovery process to map out your entire data landscape. You need to know where every piece of information lives, who uses it, and most importantly, how sensitive it is.
Once you have that full inventory, you can start classifying it. This just means tagging your data based on its importance, which helps you focus your efforts where they matter most. A common approach looks something like this:
This classification process is the bedrock of your entire security plan. It allows you to apply the tightest controls to your most valuable assets instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach that protects nothing well.
Okay, you know what data you have. Now it's time to figure out what could go wrong. A threat and risk assessment is just a systematic way of looking for potential dangers in your cloud environment. The whole point is to find your weakest links before an attacker does.
Start by brainstorming all the potential threats. These can range from external attacks like phishing and ransomware to internal risks like an employee accidentally deleting a critical folder or a malicious insider. Consider both the technical stuff, like unpatched software, and the human element, like a lack of security training.
Next, you need to weigh the risk of each threat. This comes down to two simple questions: how likely is it to happen, and how bad would it be if it did? This helps you prioritise. A low-impact threat that's highly unlikely isn't your biggest worry. A high-impact threat that's very likely to occur? That’s where you need to focus your money and effort. For smaller teams, this step is absolutely vital; you can find more tailored guidance in our article on cloud storage for small business.
Now that you know what you're protecting and what you're protecting it from, you can finally start picking your tools. Your cloud provider (like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) offers a whole suite of native security solutions, and these are often the best place to start. They're built right into the platform and can cover a lot of ground, from identity management to network security.
However, you might find you have specific gaps that require third-party tools for an extra layer of defence. This could be an advanced threat detection system, data loss prevention (DLP) software, or a specialised tool for monitoring compliance. The key is to choose solutions that directly address the risks you uncovered back in Phase 2.
Always start with a pilot programme when implementing a new tool. Test it in a controlled environment with a small group before rolling it out to the entire organisation. This lets you iron out any kinks and make sure it plays nicely with your existing systems without grinding business to a halt.
To make sure your implementation follows proven strategies, it's worth reviewing the best practices for protecting your data in the cloud as a guide.
Let's be realistic: no security system is completely foolproof. Sooner or later, an incident will happen. What separates a minor hiccup from a full-blown catastrophe is having a clear, well-rehearsed incident response (IR) plan. This is your playbook for exactly what to do when things go wrong.
The infographic below shows how a good recovery strategy works, focusing on automated backups and getting back online fast.
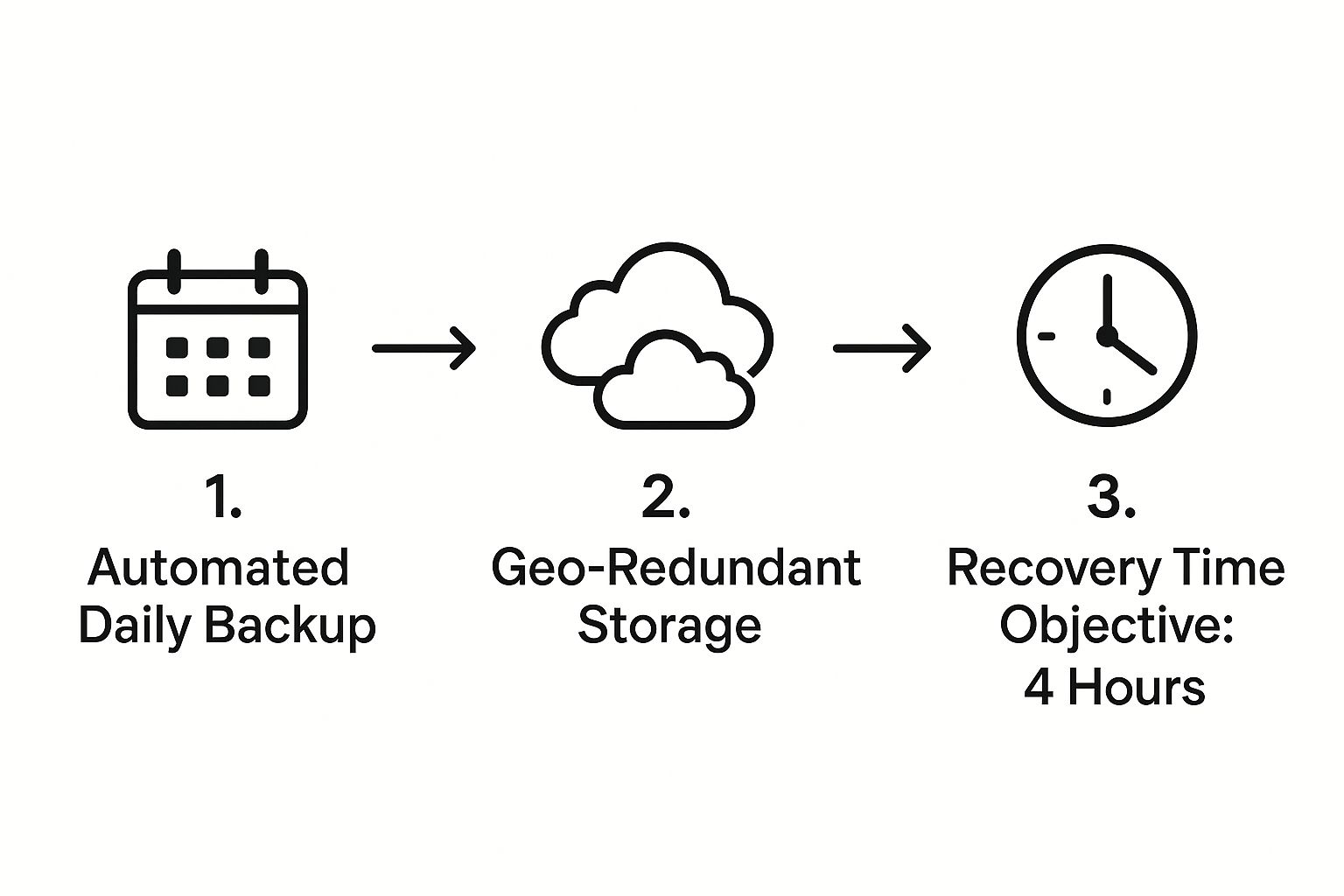
This flow shows how regular, automated backups, stored in different locations, allow for a rapid recovery time, minimising the painful downtime after an incident.
A truly useful IR plan must define:
Your IR plan should be a living document, not something that collects dust on a shelf. Test it regularly with drills and update it whenever your environment changes. A plan that goes unread is arguably worse than having no plan at all.
When it comes to cloud data protection, there are a lot of myths and a few confusing truths floating around. Let's tackle some of the most common questions head-on to give you the clarity you need to build a security strategy that actually works.
Not on its own, no. This is one of the biggest and most dangerous misconceptions out there. Big names like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all use what’s called a "Shared Responsibility Model." They handle the security of the cloud—meaning their physical data centres, the servers, and the network are locked down tight. But you are always responsible for security in the cloud.
Think of it like renting a space in a high-security bank vault. The bank guarantees the building is guarded and the walls are unbreakable. However, you're the one holding the key to your safety deposit box. You decide who gets a copy and you have to make sure you lock it when you leave. Simply trusting the provider to protect your data is a common and often very expensive mistake.
Your access controls. Period. Before you worry about anything else, lock down who can get in. This means setting up strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) and, most importantly, enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for every single user, especially your administrators.
Why is this so critical? Because stolen credentials are still the number one way hackers get in. All the fancy encryption in the world won’t help you if a bad actor can just log in with a stolen password and turn it all off. Securing the front door is the foundation for everything else.
It's easy to imagine that the biggest threats are from complex, sophisticated attacks. The reality? Over 80% of hacking-related breaches involve compromised credentials. This isn't just a best practice—MFA is an absolute necessity.
This is a great question because the two are related but serve very different functions. It's easy to mix them up.
In short: backups recover your data, while a DR plan recovers your entire business.
Data location, or data residency, is hugely important if you do business internationally. It all comes down to a complicated web of global privacy laws. Regulations like GDPR in Europe have strict rules about how the personal data of their citizens is handled, and that often means the data must physically stay within certain geographical borders.
For example, if you’re a UK business with customers in Germany, you might be legally required to store their data inside the EU. Cloud providers make this possible by letting you choose the specific region where your data lives. This allows you to create geo-targeted landing pages and services that respect local laws, which is crucial for conversion optimisation per region because customers trust businesses that respect their data privacy.
Ignoring these rules can lead to massive fines and a serious loss of trust. And when you share that data, doing so securely is just as vital. Our guide on how to share files securely offers practical steps to protect your information as it moves.
Ready to take control of your cloud data? Sky Drive Folder offers a secure, reliable platform with robust AES-256 encryption and customisable sharing controls to keep your files protected. Start storing, sharing, and securing your data with confidence today at https://skydrivefolder.com.
[…] A rock-solid cloud DLP strategy is built on a few fundamental pillars. Each one plays a unique role in creating a protective shield around your digital information. For a deeper dive into the wider world of data security, you can read our complete guide on cloud data protection. […]
[…] backup systems. For more detailed information, you can read the full article by following this link. Sign up for Private, Affordable Cloud Storage, Encrypted, Ad-Free, Forever, keep your files safe, […]
[…] business data in the cloud. You can read more about these strategies by visiting the article at Top Cloud Data Protection Tips. Sign up for Private, Affordable Cloud Storage, Encrypted, Ad-Free, Forever, keep your files safe, […]