Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA
Address
Australia, Singapore, and USA

Learn how encrypted file sharing secures your data. This guide explains how it works, its benefits, and the best practices for choosing a secure service.
Think of encrypted file sharing as sending a valuable package through a courier. Instead of just handing them an open document, you first lock it in a briefcase, and only the person you're sending it to has the key. This is the essence of encrypted file sharing: it turns your files into a secret code before they ever leave your computer, making them completely unreadable to anyone snooping around.

At its heart, encrypted file sharing is all about making sure your private data stays private—from the moment you hit "send" until your recipient opens it. This isn't just about putting a password on a folder. It’s a much more robust process that fundamentally scrambles your data into an unreadable format called ciphertext.
Let’s say you need to send sensitive financial documents to your accountant. Without encryption, shooting that file across the internet is like passing a handwritten note across a crowded room. Anyone who intercepts it can read every word.
But with encrypted file sharing, that note is first translated into a complex language that only you and your accountant can understand. Even if someone manages to grab it mid-air, all they’ll see is a bunch of gibberish.
A common mistake is thinking your files are only at risk while they’re flying across the internet. The truth is, data stored on a server—even for a short time—is a prime target for attackers.
Truly effective encrypted file sharing protects your data throughout its entire lifecycle:
By scrambling data both as it moves and while it's stored, encrypted file sharing provides a comprehensive security shield. It's a non-negotiable layer of defense in an environment where data breaches are increasingly common and costly.
This two-pronged approach is what makes the process so powerful. As businesses handle more and more sensitive information, mastering secure online file transfer is no longer a "nice-to-have"—it's critical for maintaining client trust and meeting compliance standards. It transforms file sharing from a potential risk into a secure, controlled, and professional process.
To really get a feel for how encrypted file sharing shields your data, let's skip the dense technical manuals and focus on what’s actually happening. At its heart, encryption is the art of taking readable information (known as plaintext) and scrambling it into a completely unreadable mess (ciphertext) using a secret key. Without the right key, the file is just digital gibberish.
Think of it like a secret language you invent with a friend. You write a message, then use a special dictionary (that’s your key) to swap every word for a code word. Only someone with an identical copy of that dictionary can translate the message back into something that makes sense. This simple idea is the bedrock of secure file sharing.
When it comes to this "translation" process, there are two main ways to do it, each with its own job to do.
The first and most direct method is symmetric encryption. In this setup, a single, secret key is used for both locking (encrypting) and unlocking (decrypting) the file.
Imagine you and a colleague need to share sensitive project files. You put the documents in a high-security briefcase, lock it with a one-of-a-kind physical key, and send it over. Now you have a new problem: how do you get an identical copy of that key to your colleague safely? Both of you need the exact same key to open the briefcase.
That’s symmetric encryption in a nutshell. It’s incredibly fast and efficient, which makes it perfect for encrypting big files or even an entire hard drive. Its biggest weakness, though, is key distribution. How do you securely share the key without someone intercepting it? Sending the key along with the locked file would completely defeat the purpose.
This is where asymmetric encryption steps in with a clever fix for the key-sharing headache. Instead of just one key, this method uses a pair of keys that are mathematically tied together.
It’s like having a personal mailbox right at your front door. The mail slot (your public key) is open for anyone to drop a letter inside. But only you have the unique key (your private key) that can actually open the mailbox and read the letters. Someone can use your public key to lock a file, but once it’s locked, only your private key can ever unlock it. This system brilliantly solves the key distribution problem because your secret key never has to travel anywhere.
Key Insight: Most modern encrypted file sharing platforms use a hybrid model. They leverage the slower but more secure asymmetric method to safely share a temporary, one-time-use symmetric key. Then, they use that lightning-fast symmetric key to encrypt the actual file. It’s the best of both worlds—the ironclad security of asymmetric keys and the speed of symmetric ones.
True security isn't just about protecting a file while it flies across the internet. A complete strategy protects your data no matter where it is or what it's doing. You'll often hear terms like "end-to-end encryption" or "at-rest encryption." These aren't just marketing buzzwords; they describe critical layers of your data's defense.
| Encryption State | What It Protects | Common Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| In-Transit Encryption | Your data as it travels from your device to a server and on to the recipient. | An armored truck moving valuables between two secure locations. |
| At-Rest Encryption | Your data while it’s stored on a server or hard drive. | Valuables locked away inside a bank vault at the destination. |
| End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) | Your data for the entire journey, from sender to recipient, so no one in between—not even the service provider—can read it. | A letter locked in a box where only the sender and recipient have keys. The delivery service can't peek inside. |
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is widely considered the gold standard for encrypted file sharing. It guarantees that from the moment you hit "send" until your recipient opens the file, your data remains completely unreadable to everyone else. This includes hackers, government agencies, and even the company whose file-sharing service you're using. This "zero-knowledge" approach gives you the ultimate say over who sees your most sensitive information.

It’s one thing to know how encryption works, but it’s another to see what it actually does for you. Using encrypted file sharing isn't just some technical box-checking exercise. It’s a smart business move that delivers real-world advantages, turning security from a vague idea into a concrete asset that protects your work, your reputation, and your bottom line.
The most obvious win is total data privacy. When you encrypt a file, you're essentially locking it in a digital vault. Even if a hacker breaches your server or intercepts a file on its journey, all they get is a garbled, useless mess of data. This is the bedrock of keeping sensitive information away from prying eyes.
In many jobs, confidentiality isn't just a professional courtesy—it's the law. A law firm, for example, is constantly handling privileged client information and sensitive case files. A leak could shatter attorney-client privilege, leading to serious legal trouble and financial fallout.
By using an encrypted file sharing service, that firm makes sure documents for a secret merger or a high-profile case are completely unreadable to anyone outside the small circle of approved people. The same goes for a healthcare provider sharing patient records or a financial advisor sending over investment strategies.
This isn’t a niche concern, either. The global market for secure file transfer, which is built on encryption, is projected to swell to USD 3.63 billion by 2029, growing at a steady clip of nearly 9.7% each year. This boom shows that businesses everywhere are realizing secure data sharing is no longer a "nice-to-have."
Beyond just following the rules, encryption is your best defense for protecting creative and strategic assets. Imagine a design agency collaborating with a freelancer on a new brand identity for a huge client. The logo concepts, marketing plans, and product mockups are all priceless intellectual property (IP).
If they shared those files over an unsecured channel, a competitor could snatch them, steal their ideas, and launch a look-alike campaign before they ever get the chance. Encryption acts as the digital lockbox for that IP.
By using end-to-end encryption, the agency guarantees that only the client and the authorized designer can see the work in progress. This protects their creative investment and keeps the big reveal under wraps until launch day.
This protection is vital for any organization creating unique assets:
Many industries are governed by tough data protection laws that come with massive fines for breaking them. Frameworks like GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the U.S. demand that organizations use strong technical safeguards to protect personal data.
Using an encrypted file sharing solution is a huge first step toward meeting these demands. It gives you a clear, auditable record showing you took proactive steps to lock down sensitive information. This is non-negotiable for organizations in:
For any business handling sensitive information, getting a handle on the best practices for secure document sharing is essential for steering clear of expensive fines and earning the trust of your clients.
To really trust encrypted file sharing, you have to know what’s going on under the hood. The magic comes from something called encryption protocols—basically, the strict sets of rules that scramble your data so no one else can read it. The technology itself gets complicated, but the main ideas are surprisingly simple. Let’s break down the heavy hitters you’ll see mentioned most often.
Think of it like a security team with different specialists. You don't just have one guard at the door; you have a team where each member has a specific, critical job. For modern data protection, these protocols work together to build a layered defense for your files.
First on the scene is Transport Layer Security (TLS), the modern version of the older Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). TLS is what creates a secure, private tunnel for your data to travel through on the internet. It’s the protocol that puts the "s" in "https" and gives you that little padlock icon in your browser's address bar.
When you send a file using a secure service, TLS is your first line of defense. It makes sure the server you're connecting to is the real deal (and not an imposter) before creating an encrypted link between your computer and that server. Its main job is protecting your data in transit so no one can eavesdrop while it's on the move.
Once your file is traveling through that secure TLS tunnel, it needs its own personal lock. That’s where the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) steps in. AES is what’s known as a symmetric encryption algorithm, which is a fancy way of saying it uses the same single key to both lock and unlock your data.
AES is the gold standard for securing data at rest—when it's just sitting on a server or a hard drive. It's famous for being incredibly fast and efficient, which makes it perfect for encrypting large files or even entire disks without grinding everything to a halt. The U.S. government even trusts AES to protect classified information, which tells you everything you need to know about its strength.
Key Insight: You'll often see AES mentioned with numbers like AES-128 and AES-256. That number just refers to the length of the key in bits. A 256-bit key offers a mind-boggling number of possible combinations, making it computationally impossible to crack with any current technology. It would take the world's most powerful supercomputers billions of years to guess the key.
This brings us to RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), a clever asymmetric algorithm that solves one major puzzle: how do you safely share the secret key that AES needs to work? RSA uses a pair of keys—a public key that anyone can use to lock data, but only a corresponding private key can unlock it.
In an encrypted file sharing system, RSA often plays the role of the "secure handshake." It’s used to safely pass the symmetric AES key between the sender and the recipient. Because it’s much slower than AES, it’s not used to encrypt the whole file. Instead, it just encrypts the small but crucial AES key, making sure only the right person can get it and unlock the main file.
This infographic shows the practical differences between AES and RSA, highlighting how they're optimized for very different jobs.
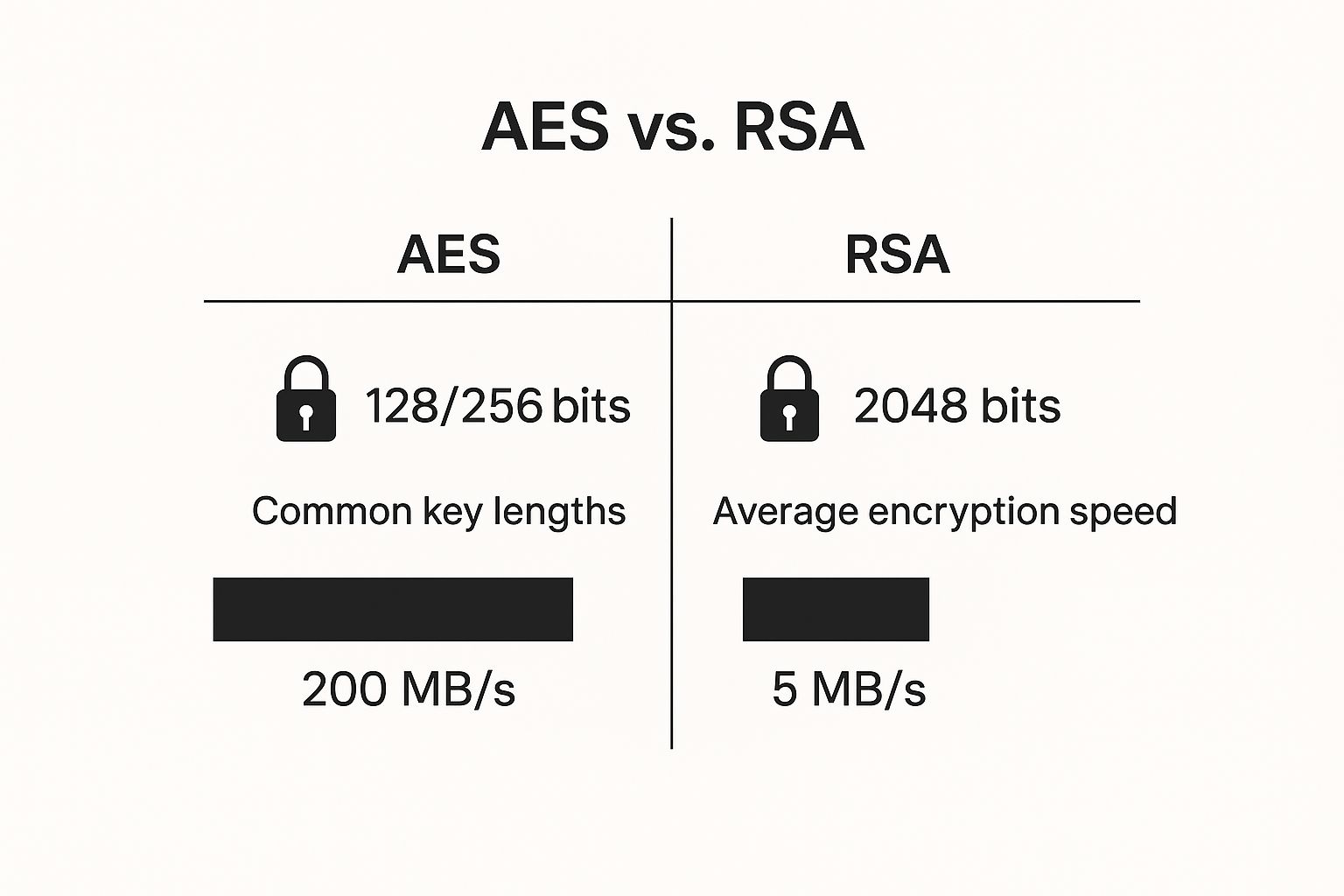
As you can see, AES is built for speed and efficiency when dealing with large amounts of data. RSA, on the other hand, prioritizes robust security for the key exchange itself, not raw performance. These protocols aren’t competing; they're designed to work together as a team.
To help you get a clearer picture of the landscape, here's a quick breakdown of these common protocols.
This table breaks down the essential features, primary use cases, and key strengths of the most common encryption protocols used in secure file sharing.
| Protocol | Type | Primary Use Case | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLS | Hybrid | Securing data in transit over a network (e.g., HTTPS) | Provides a secure "tunnel" and server authentication. |
| AES | Symmetric | Encrypting data at rest (stored on a disk or server) | Extremely fast and efficient for encrypting large files. |
| RSA | Asymmetric | Securely exchanging the symmetric (AES) key | Extremely strong key exchange; prevents key interception. |
Each protocol fills a specific role, and a truly secure file sharing system will use all of them in concert. TLS creates the safe path, RSA hands over the keys securely, and AES locks up the file itself. Understanding how they work together is the first step toward choosing a service you can truly trust.
Picking the right platform for encrypted file sharing can feel overwhelming, but it doesn't have to be. Once you have a clear picture of what you need, you can cut through the marketing fluff and find a service that nails the right mix of security, ease of use, and control. Not every tool is built the same, so let’s walk through what separates a basic uploader from a truly secure one.
Think of it like choosing a safe for your valuables. You wouldn't use a cheap hotel room safe to protect priceless heirlooms; you'd want a heavy-duty, fireproof vault. The right choice depends entirely on what you're protecting and from whom. A freelance journalist sending interview notes has different needs than a financial firm processing thousands of client transactions a day.
This is exactly why the market for these solutions is booming. The global secure file transfer market, which includes encrypted file sharing, was valued at around USD 2.4 billion in 2024 and is expected to climb to USD 3.7 billion by 2033. This growth is all about the rising demand for services that offer serious encryption and detailed tracking. You can discover more about the factors driving this expansion by reading the full secure file transfer market analysis.
Before you even glance at pricing or storage limits, your first priority has to be a rock-solid security foundation. If a service can’t guarantee the privacy of your data, nothing else matters. Use this checklist as your starting point to vet any provider you're considering.
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): This is the gold standard, no question. It means your files are encrypted on your device and can only be decrypted by your intended recipient. The service provider can't even access your data. This "zero-knowledge" approach is critical for maximum privacy.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Passwords just aren't enough anymore. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification—like a code sent to your phone—making it much harder for someone to break into your account.
Detailed Audit Logs and Tracking: You need to know who is accessing your files and when. A good service provides detailed logs that track every single view, download, and share, giving you total visibility and control over your data's entire lifecycle.
Key Takeaway: Real security isn't about a single feature; it's about a layered defense. A platform that combines E2EE, MFA, and comprehensive audit trails creates a powerful shield for protecting your most sensitive information from all angles.
Once you've confirmed the core security is there, the next step is to find features that fit how you actually work. A clunky, confusing interface can ruin an otherwise powerful tool. You want a service that makes secure sharing a seamless part of your daily routine, not a frustrating chore you have to fight with.
Consider these practical features:
Granular Access Controls: Can you set specific permissions for each shared link? Look for the ability to set expiration dates, limit the number of downloads, and require a password for access. This stops your sensitive files from living on the internet forever.
Large File Support: Creative pros, researchers, and video producers deal with massive files all the time. Make sure the service can handle the file sizes you work with without choking. For a deeper look at this, check out our guide on how to transfer large files efficiently and safely.
Intuitive User Interface (UI): Security shouldn't come at the cost of usability. A clean, easy-to-navigate interface means you and your team will actually use the security features correctly, which is the best way to minimize human error.
Ultimately, the goal is to find a service that fits your specific use case. A small business might prioritize collaboration features and audit logs for compliance, while a solo user might care more about generous storage and ease of use. By mapping your needs to these critical features, you can make a smart choice that truly protects your data.

Even the most powerful encrypted file sharing platform is only as strong as the person using it. Think of it this way: the encryption algorithms build the vault, but your daily habits are what keep the door locked. Getting a few simple, intentional practices right can dramatically cut down the risk of human error and make sure your sensitive data stays that way.
The goal is to develop good muscle memory for security, turning these actions into second nature. When secure sharing becomes a routine instead of a chore, you and your team become the strongest line of defense.
The second you generate a shareable link, you’ve created a new potential key to your data. Leaving links active forever is like leaving that key under the doormat—it's convenient, but it’s just asking for trouble. Smart link management is the first and most critical habit to master.
Before you share anything important, always take a moment to configure these settings:
Security is a team sport. These small, proactive steps reinforce that everyone has a role to play in protecting information. They help you avoid common mistakes and minimize risks that even the best technology can't prevent on its own.
Technology can’t replace simple human diligence. Before you hit "send" on highly sensitive data, just take a moment to confirm you have the right recipient. A simple typo in an email address could accidentally send confidential information to a complete stranger.
Confirming the recipient's identity is a basic but essential step. A quick follow-up message or call can prevent a disastrous mistake, especially when you're dealing with new clients or external partners for the first time.
And always be on guard for phishing scams. These attacks are designed to trick you into giving up login details or downloading malware by pretending to be legitimate services. Be skeptical of unexpected requests for files or sudden password reset alerts. If you want to dive deeper, our complete guide to secure file sharing offers more strategies. By staying vigilant and treating every share with care, you build a resilient defense against both accidental exposure and targeted attacks.
Even after you get a handle on how encrypted file sharing works, a few common questions always seem to surface. Answering these is the final piece of the puzzle, helping you feel completely confident in the security tools you’re using. Let’s clear up a few lingering doubts and popular myths.
Getting this right is more important than ever, as this technology becomes a standard part of business. The global encryption software market was valued at over USD 13.5 billion in 2024, and it’s growing fast, largely because of the boom in cloud services and very real concerns over data breaches. You can learn more about what’s driving this growth in this detailed encryption software market forecast.
While no system is 100% perfect, modern encryption standards like AES-256 are, for all practical purposes, unbreakable with today's computers. Seriously, it would take the world’s fastest supercomputers billions of years to brute-force the key.
But the real-world security of your files often comes down to things beyond the encryption itself. The weakest links are almost always human. A platform might have a poor implementation, or a user might choose a weak password or fall for a phishing scam. The math behind the encryption is rock-solid; it’s human error that usually creates the vulnerability.
Sure, services like Google Drive or Dropbox do encrypt your files. They protect them "in transit" (as they travel over the internet) with TLS and "at rest" (while sitting on their servers). The critical difference, though, is that the provider usually holds onto the encryption keys. This means, if they were legally required to, they could technically access your data.
For absolute privacy and control, what you really need is a service that offers end-to-end encryption (E2EE) or a "zero-knowledge" model. This setup guarantees that only you and your intended recipient have the keys, making your files completely unreadable to everyone else—including the people who run the service.
This is a really common point of confusion, but the distinction is huge. Think of it like securing a house.
A truly secure file needs both. The password stops unauthorized entry, but the encryption protects the actual data. Even if someone manages to kick down the door, all they’ll find inside is gibberish without the unique encryption key. This is especially vital when dealing with large assets, a point we touch on in our guide on how to share large video files. Real security means protecting both the container and what's inside it.
Ready to share files with confidence and total control? Sky Drive Folder offers robust AES-256 encryption, password-protected links, and detailed access controls to keep your sensitive data secure from end to end. Start sharing securely today.
[…] more insights on how to enhance your cloud storage security, you can read this related article on encrypted file sharing and secure private data transfer. This resource offers valuable information on maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of your […]